Chapter 8 Aligned individual-level and population-level task directed evolution experiment
8.1 Overview
Supplemental information and data analyses for the directed evolution experiment where rewards for individual- and population-level tasks are aligned.
8.2 Analysis dependencies
Load all required R libraries
library(tidyverse)
library(ggplot2)
library(cowplot)
library(RColorBrewer)
library(khroma)
source("https://gist.githubusercontent.com/benmarwick/2a1bb0133ff568cbe28d/raw/fb53bd97121f7f9ce947837ef1a4c65a73bffb3f/geom_flat_violin.R")These analyses were knit with the following environment:
## _
## platform x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
## arch x86_64
## os linux-gnu
## system x86_64, linux-gnu
## status
## major 4
## minor 2.1
## year 2022
## month 06
## day 23
## svn rev 82513
## language R
## version.string R version 4.2.1 (2022-06-23)
## nickname Funny-Looking Kid8.3 Setup
Load experiment summary data.
exp_summary_data_loc <- paste0(working_directory,"data/experiment_summary.csv")
exp_summary_data <- read.csv(exp_summary_data_loc, na.strings="NONE")
exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD <- factor(
exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
levels=c(
"elite",
"elite-10",
"tournament",
"lexicase",
"non-dominated-elite",
"random",
"none"
),
labels=c(
"elite",
"elite-10",
"tourn",
"lex",
"nde",
"random",
"none"
)
)Load time series data.
times_series_data_loc <- paste0(working_directory,"data/evaluation_time_series_corrected.csv")
times_series_data <- read.csv(times_series_data_loc, na.strings="NONE")
# Specify experimental condition for each datum.
times_series_data$SELECTION_METHOD <- factor(
times_series_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
levels=c(
"elite",
"elite-10",
"tournament",
"lexicase",
"non-dominated-elite",
"non-dominated-tournament",
"random",
"none"
),
labels=c(
"elite",
"elite-10",
"tourn",
"lex",
"nde",
"ndt",
"random",
"none"
)
)
times_series_data$epoch_offset <- times_series_data$epoch+1Load task coverage per population data.
task_coverage_per_pop_data_loc <- paste0(working_directory,"data/max_coverage_per_pop_cnt.csv")
task_coverage_per_pop_data <- read.csv(task_coverage_per_pop_data_loc, na.strings="NONE")
# Specify experimental condition for each datum.
task_coverage_per_pop_data$SELECTION_METHOD <- factor(
task_coverage_per_pop_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
levels=c(
"elite",
"elite-10",
"tournament",
"lexicase",
"non-dominated-elite",
"non-dominated-tournament",
"random",
"none"
),
labels=c(
"elite",
"elite-10",
"tourn",
"lex",
"nde",
"ndt",
"random",
"none"
)
)Miscellaneous setup
# Configure our default graphing theme
theme_set(theme_cowplot())
# Palette
scale_fill_fun <- scale_fill_bright
scale_color_fun <- scale_color_bright
alpha <- 0.05
# Create a directory to store plots
plot_directory <- paste0(working_directory, "plots/")
dir.create(plot_directory, showWarnings=FALSE)
p_label <- function(p_value) {
threshold = 0.0001
if (p_value < threshold) {
return(paste0("p < ", threshold))
} else {
return(paste0("p = ", p_value))
}
}
selection_method_breaks <- c("elite", "elite-10", "tourn", "lex", "nde", "random", "none")
selection_method_labels <- c("ELITE", "TOP-10", "TOURN", "LEX", "NDE", "RAND", "NONE")8.4 Best single-population task coverage
max_trait_cov_fig <-
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=SELECTION_METHOD,
y=max_trait_coverage,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8,
adjust=1.5
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(height=0.1, width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Task Coverage",
limits=c(-0.5,18),
breaks=seq(0,18,2)
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_fill_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels,
) +
scale_color_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels,
) +
theme(
legend.position="none"
)
max_trait_cov_fig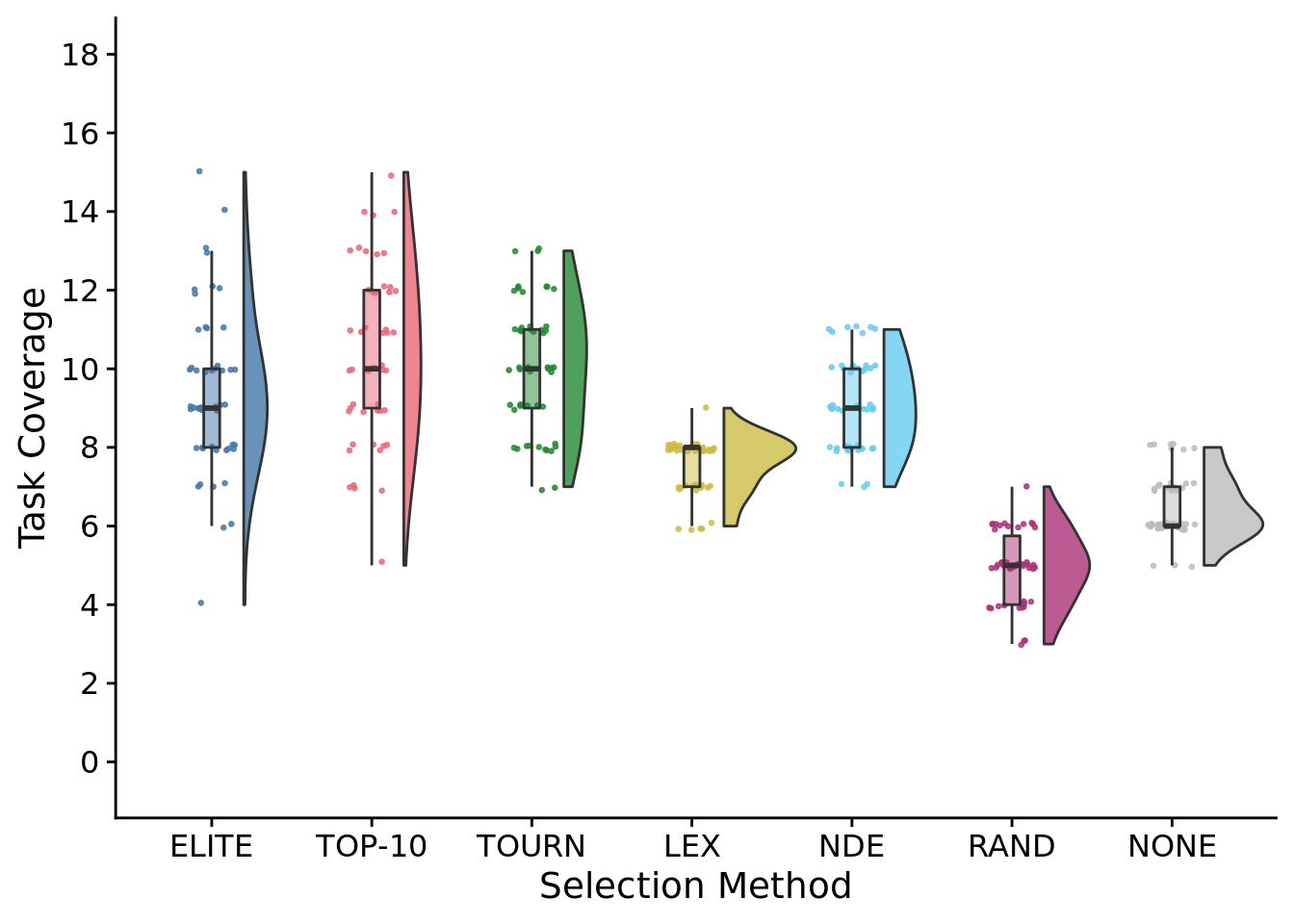
## Saving 7 x 5 in imageStatistical results:
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: max_trait_coverage by SELECTION_METHOD
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 232.92, df = 6, p-value < 2.2e-16# Kruskal-wallis is significant, so we do a post-hoc wilcoxon rank-sum.
pairwise.wilcox.test(
x=exp_summary_data$max_trait_coverage,
g=exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
p.adjust.method="bonferroni",
)##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: exp_summary_data$max_trait_coverage and exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD
##
## elite elite-10 tourn lex nde random
## elite-10 0.713 - - - - -
## tourn 1.000 1.000 - - - -
## lex 5.7e-07 5.4e-10 1.5e-11 - - -
## nde 1.000 0.056 0.098 2.0e-09 - -
## random 2.2e-15 3.6e-16 < 2e-16 2.4e-16 < 2e-16 -
## none 4.9e-12 7.1e-14 1.9e-15 7.8e-08 7.5e-15 3.6e-11
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni8.4.1 Best single-population task coverage time series
To speed up graphing, we plot a low-resolution version of the time series.
max_trait_cov_ot_fig <-
ggplot(
# times_series_data,
filter(times_series_data, (epoch_offset%%10)==0 | epoch_offset==1),
aes(
x=epoch_offset,
y=max_trait_coverage,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD,
color=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
stat_summary(geom="line", fun=mean) +
stat_summary(
geom="ribbon",
fun.data="mean_cl_boot",
fun.args=list(conf.int=0.95),
alpha=0.2,
linetype=0
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Cycle"
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Task Coverage",
limits=c(-0.5,18),
breaks=seq(0,18,2)
) +
scale_fill_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_color_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
theme(
legend.position="bottom"
)
max_trait_cov_ot_fig## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`: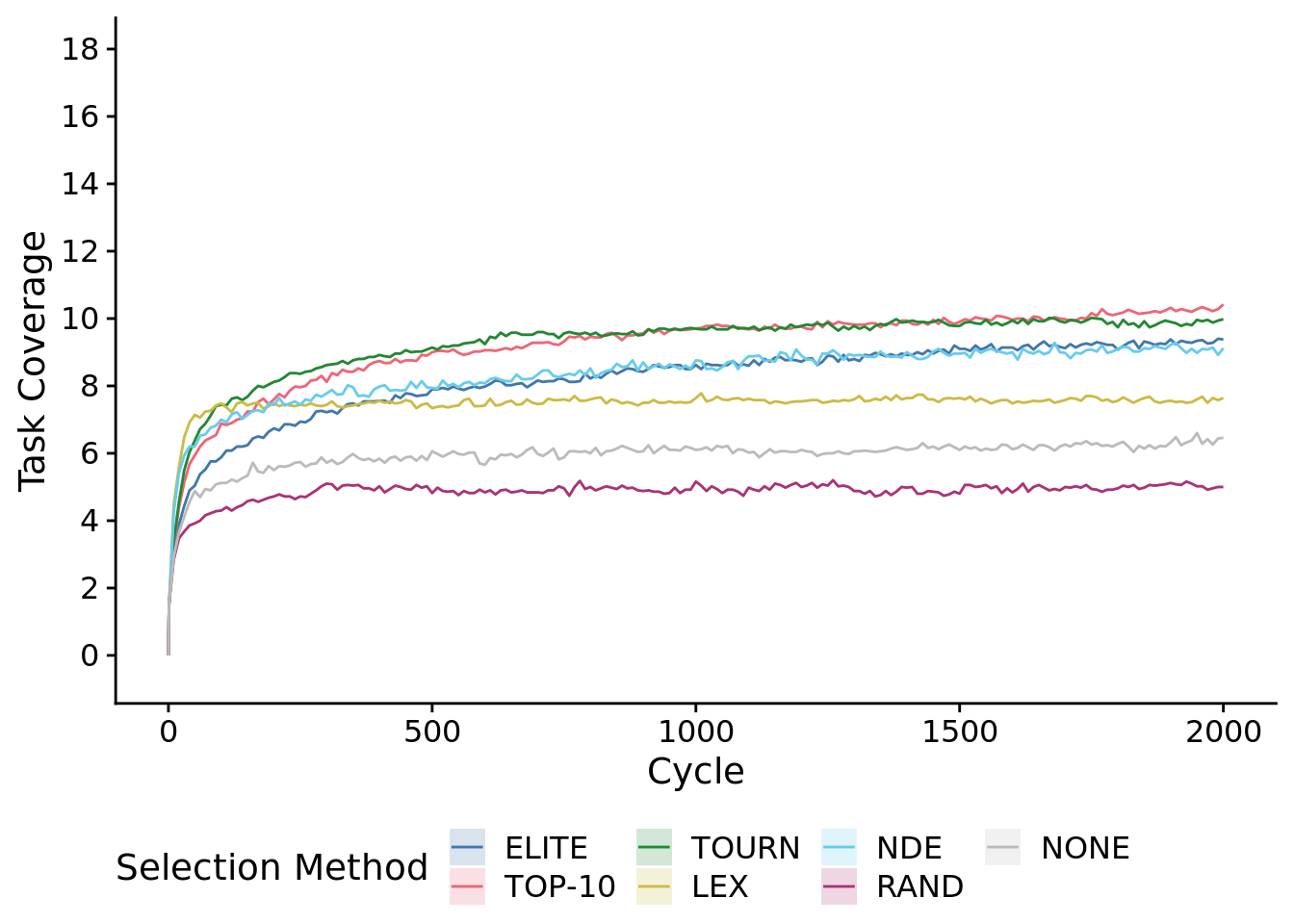
ggsave(
plot=max_trait_cov_ot_fig,
filename=paste0(plot_directory, "2021-11-30-best-pop-task-cov-ts.pdf"),
width=10,
height=6
)## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`:8.4.1.1 First 30 cycles of the experiment
max_trait_cov_ot_early_fig <-
ggplot(
# times_series_data,
filter(times_series_data, (epoch_offset <= 30)),
aes(
x=epoch_offset,
y=max_trait_coverage,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD,
color=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
stat_summary(geom="line", fun=mean) +
stat_summary(
geom="ribbon",
fun.data="mean_cl_boot",
fun.args=list(conf.int=0.95),
alpha=0.2,
linetype=0
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Cycles"
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Task Coverage",
limits=c(-0.5,18.5),
breaks=seq(0,18,2)
) +
scale_fill_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_color_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
theme(
legend.position="bottom"
)
max_trait_cov_ot_early_fig## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`: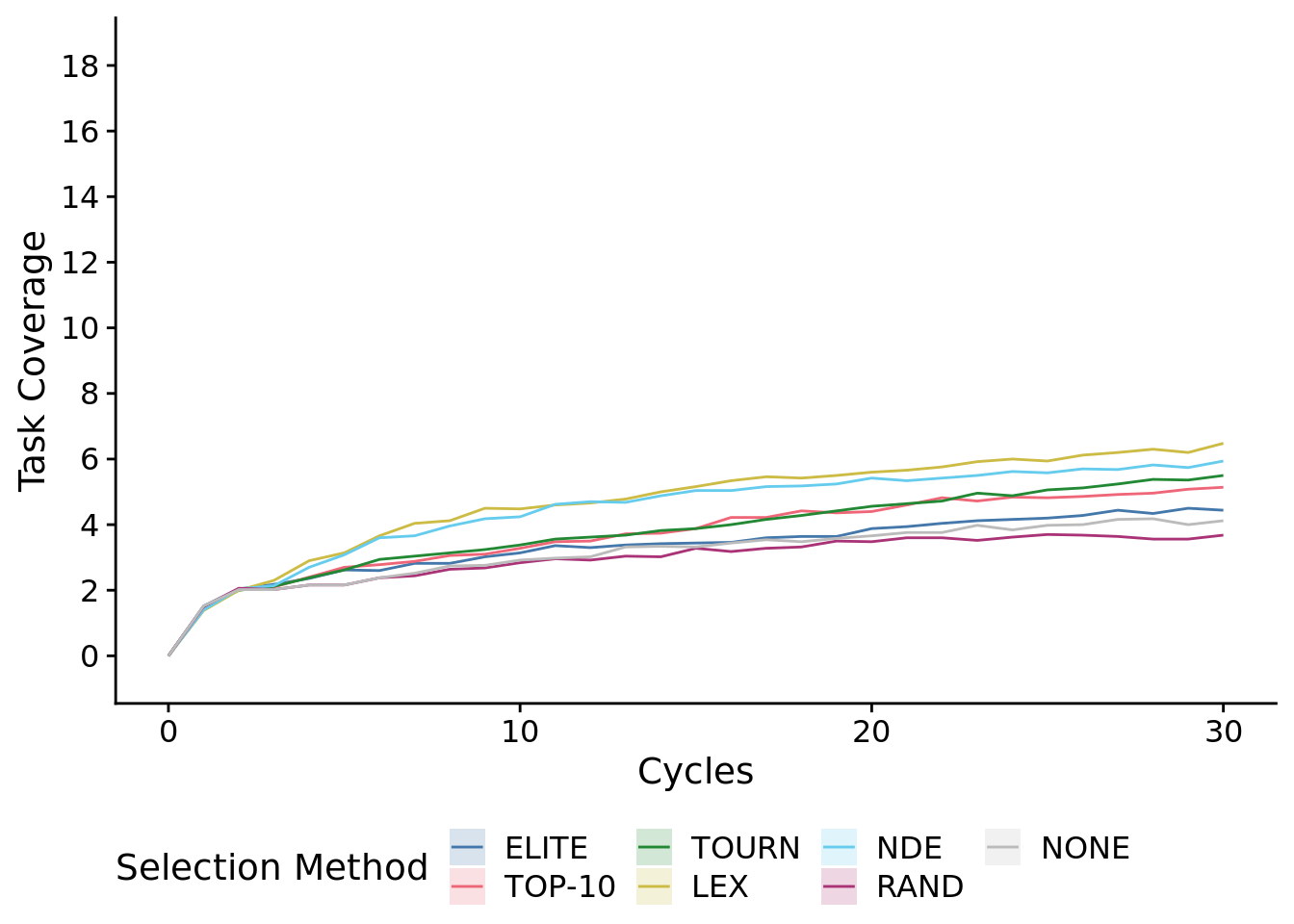
ggsave(
filename=paste0(plot_directory, "2021-11-30-best-pop-task-cov-ts-early.pdf"),
width=10,
height=6
)## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`:8.5 Metapopulation task coverage
total_trait_cov_fig <-
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=SELECTION_METHOD,
y=total_trait_coverage,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8,
adjust=1.5
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(height=0.1, width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Task Coverage",
limits=c(-0.5,18.5),
breaks=seq(0,18,2)
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_fill_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_color_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
theme(
legend.position="none"
)
total_trait_cov_fig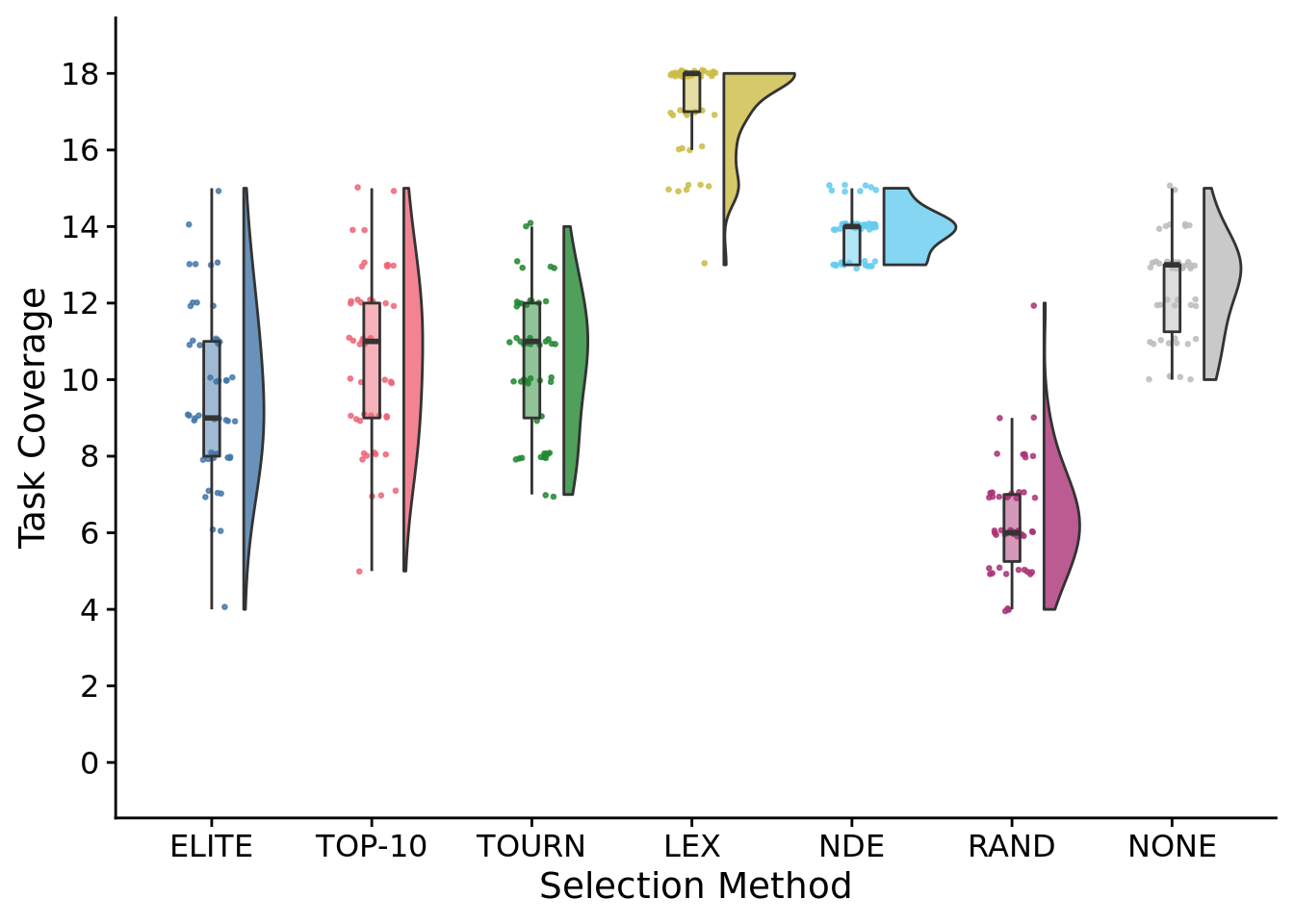
## Saving 7 x 5 in imageStatistical results:
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: total_trait_coverage by SELECTION_METHOD
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 269.5, df = 6, p-value < 2.2e-16# Kruskal-wallis is significant, so we do a post-hoc wilcoxon rank-sum.
pairwise.wilcox.test(
x=exp_summary_data$total_trait_coverage,
g=exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
p.adjust.method="bonferroni",
)##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: exp_summary_data$total_trait_coverage and exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD
##
## elite elite-10 tourn lex nde random
## elite-10 1.00000 - - - - -
## tourn 1.00000 1.00000 - - - -
## lex < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 - - -
## nde 2.2e-14 2.6e-12 6.9e-15 1.1e-15 - -
## random 7.7e-11 5.6e-13 6.2e-14 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 -
## none 2.2e-08 0.00014 3.1e-06 < 2e-16 4.9e-08 < 2e-16
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni8.5.1 Metapopulation task coverage time series
To speed up graphing, we plot a low-resolution version of the time series.
metapop_task_cov_ot_fig <-
ggplot(
# times_series_data,
filter(times_series_data, (epoch_offset%%10)==0 | epoch_offset==1),
aes(
x=epoch_offset,
y=total_trait_coverage,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD,
color=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
stat_summary(geom="line", fun=mean) +
stat_summary(
geom="ribbon",
fun.data="mean_cl_boot",
fun.args=list(conf.int=0.95),
alpha=0.2,
linetype=0
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Cycle"
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Task Coverage",
limits=c(-0.5,18.5),
breaks=seq(0,18,2)
) +
scale_fill_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_color_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
theme(
legend.position="bottom"
)
metapop_task_cov_ot_fig## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`: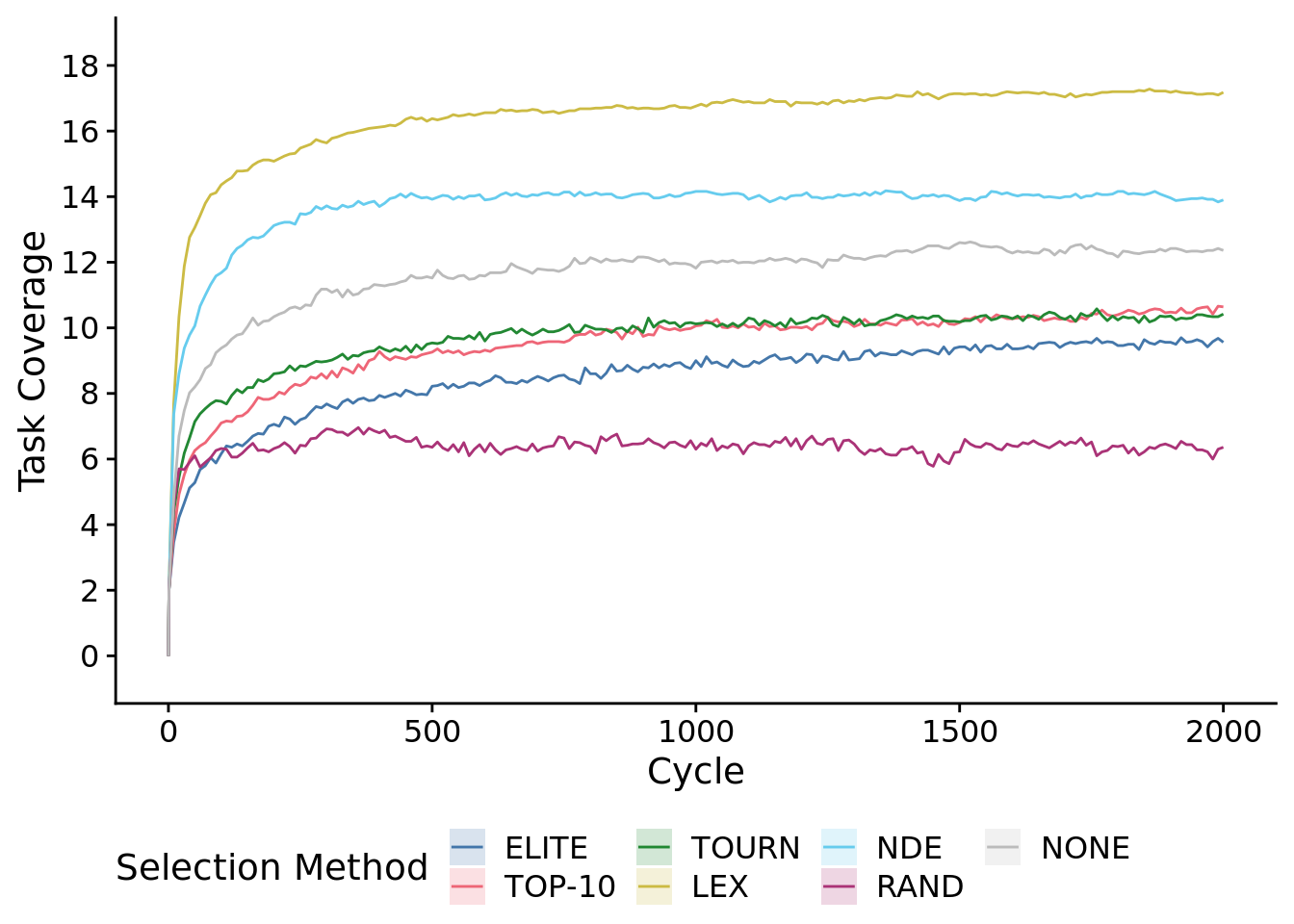
ggsave(
plot=metapop_task_cov_ot_fig,
filename=paste0(plot_directory, "2021-11-30-metapop-task-cov-ts.pdf"),
width=10,
height=6
)## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`:8.5.1.1 First 30 cycles of the experiment
metapop_task_cov_ot_early_fig <-
ggplot(
# times_series_data,
filter(times_series_data, (epoch_offset <= 30)),
aes(
x=epoch_offset,
y=total_trait_coverage,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD,
color=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
stat_summary(geom="line", fun=mean) +
stat_summary(
geom="ribbon",
fun.data="mean_cl_boot",
fun.args=list(conf.int=0.95),
alpha=0.2,
linetype=0
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Cycles"
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Task Coverage",
limits=c(-0.5,18.5),
breaks=seq(0,18,2)
) +
scale_fill_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_color_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
theme(
legend.position="bottom"
)
metapop_task_cov_ot_early_fig## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`: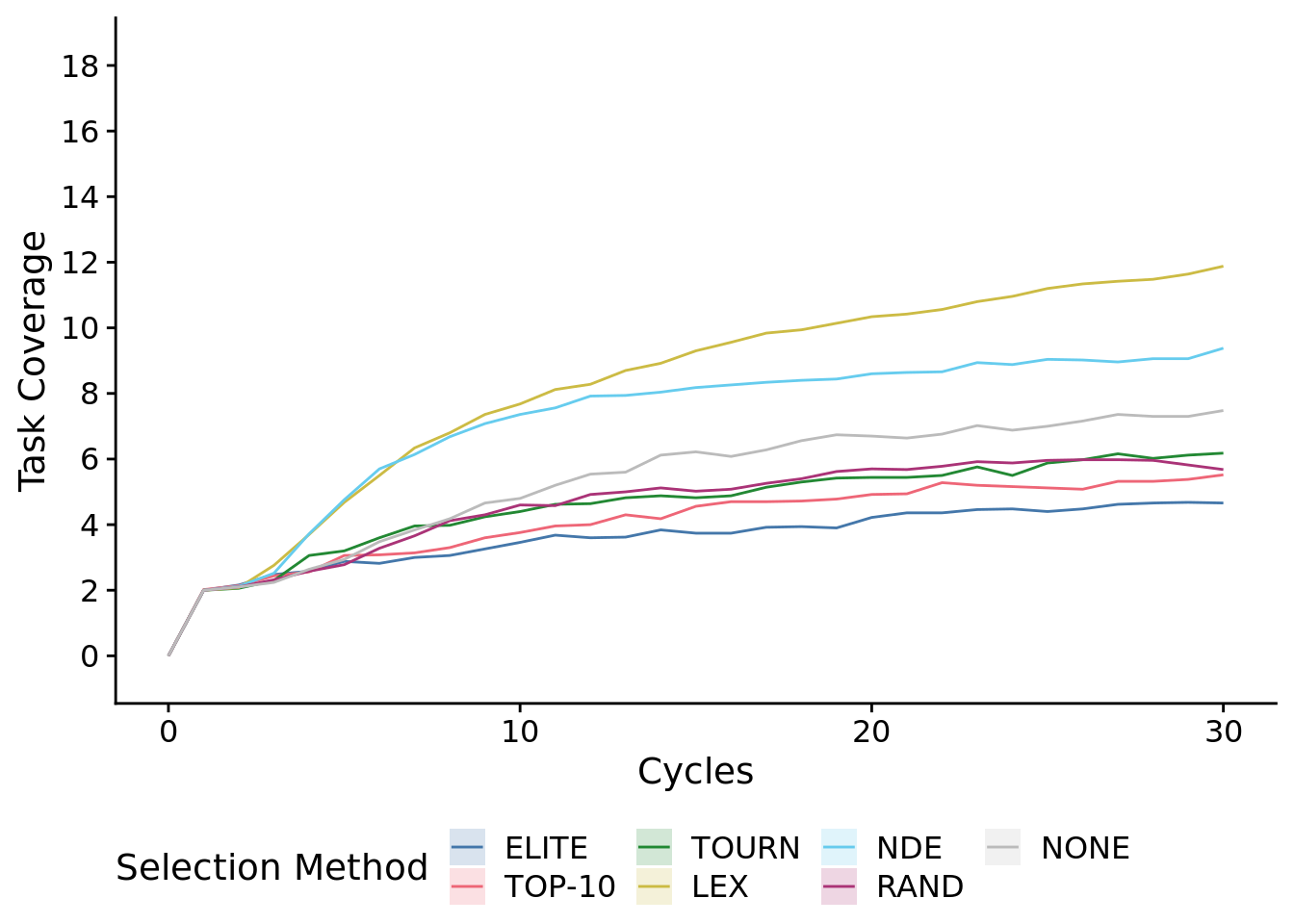
ggsave(
filename=paste0(plot_directory, "2021-11-30-metapop-task-cov-ts-early.pdf"),
width=10,
height=6
)## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`:After just 10 cycles, we observed significant gains from using NDE and LEX selection protocols.
early_data <- filter(times_series_data, epoch_offset==10)
kruskal.test(
formula=total_trait_coverage~SELECTION_METHOD,
data=early_data
)##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: total_trait_coverage by SELECTION_METHOD
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 202.89, df = 6, p-value < 2.2e-16# Kruskal-wallis is significant, so we do a post-hoc wilcoxon rank-sum.
pairwise.wilcox.test(
x=early_data$total_trait_coverage,
g=early_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
p.adjust.method="bonferroni",
)##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: early_data$total_trait_coverage and early_data$SELECTION_METHOD
##
## elite elite-10 tourn lex nde random
## elite-10 1.0000 - - - - -
## tourn 0.1043 1.0000 - - - -
## lex 4.0e-16 5.5e-15 2.6e-12 - - -
## nde 3.6e-16 4.2e-15 2.5e-12 1.0000 - -
## random 5.3e-05 0.0062 1.0000 2.8e-14 4.7e-14 -
## none 9.9e-06 0.0013 1.0000 3.8e-13 3.1e-13 1.0000
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni8.6 Metapopulation task profile diversity
We measured the “phenotypic” diversity within evolved metapopulations in three ways:
- the number of task profiles (richness)
- the spread of task profiles as the average cosine distance from the centroid profile
- the Shannon entropy of task profiles
8.6.1 Number of different task profiles
num_pop_task_profiles_fig <-
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=SELECTION_METHOD,
y=num_pop_trait_profiles,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(height=0, width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="# Different Task Profiles"
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_fill_fun(
) +
scale_color_fun(
) +
theme(
legend.position="none"
)
num_pop_task_profiles_fig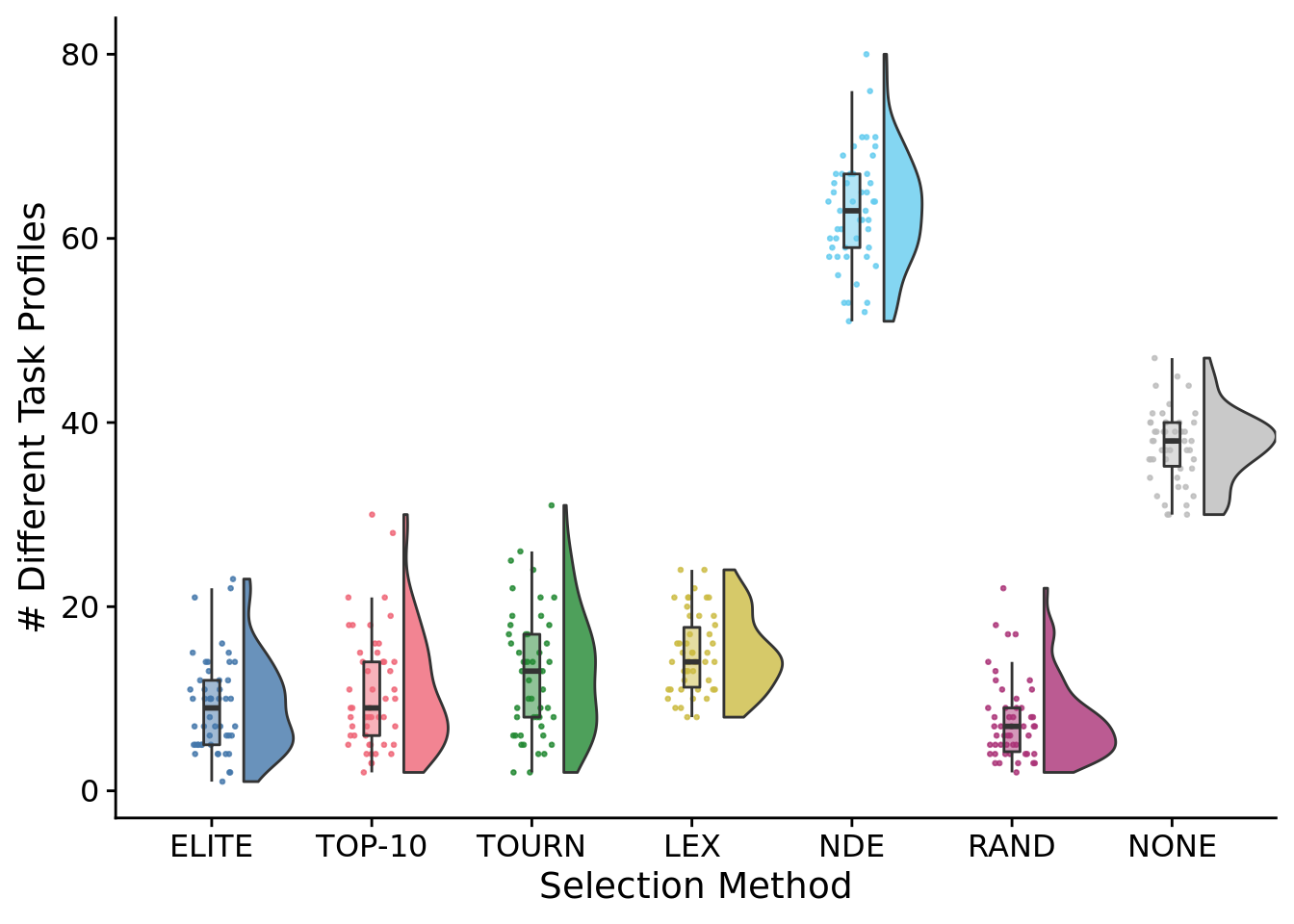
ggsave(
plot=num_pop_task_profiles_fig,
paste0(plot_directory, "2021-11-30-num-task-profiles.pdf")
)## Saving 7 x 5 in imageStatistical results
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: num_pop_trait_profiles by SELECTION_METHOD
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 247.78, df = 6, p-value < 2.2e-16# Kruskal-wallis is significant, so we do a post-hoc wilcoxon rank-sum.
pairwise.wilcox.test(
x=exp_summary_data$num_pop_trait_profiles,
g=exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
p.adjust.method="bonferroni",
)##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: exp_summary_data$num_pop_trait_profiles and exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD
##
## elite elite-10 tourn lex nde random
## elite-10 1.00000 - - - - -
## tourn 0.12006 1.00000 - - - -
## lex 9.0e-07 0.00066 0.64177 - - -
## nde < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 - -
## random 1.00000 0.19565 0.00081 2.5e-10 < 2e-16 -
## none < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni8.6.1.1 Number of different task profiles over time
To speed up graphing, we reduced the time series resolution in this plot.
num_task_profiles_ot_fig <-
ggplot(
filter(times_series_data, (updates_elapsed%%10000)==0 | updates_elapsed==1),
aes(
x=updates_elapsed,
y=num_pop_trait_profiles,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD,
color=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
stat_summary(geom="line", fun=mean) +
stat_summary(
geom="ribbon",
fun.data="mean_cl_boot",
fun.args=list(conf.int=0.95),
alpha=0.2,
linetype=0
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Updates elapsed"
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="# Different Task Profiles"
) +
scale_fill_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_color_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
theme(
legend.position="bottom"
)
num_task_profiles_ot_fig## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`: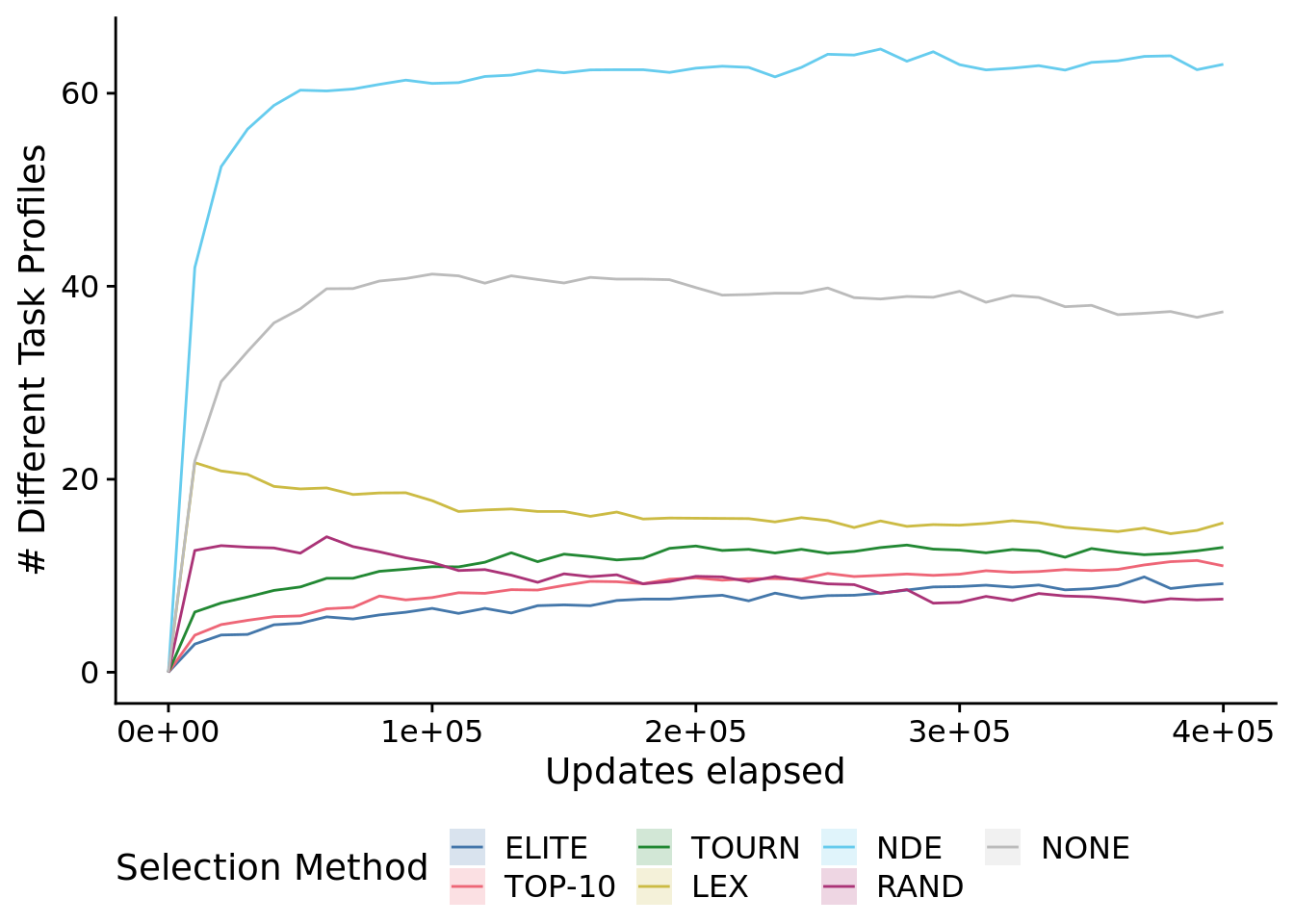
ggsave(
num_task_profiles_ot_fig,
filename=paste0(plot_directory, "2021-11-30-num-task-profiles-ts.png"),
width=10,
height=6
)## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`:8.6.2 Task profile spread
task_profile_spread_fig <-
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=SELECTION_METHOD,
y=avg_cosine_dist_from_centroid,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(height=0, width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Avg. Task Spread"
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_fill_fun(
) +
scale_color_fun(
) +
theme(
legend.position="none"
)
task_profile_spread_fig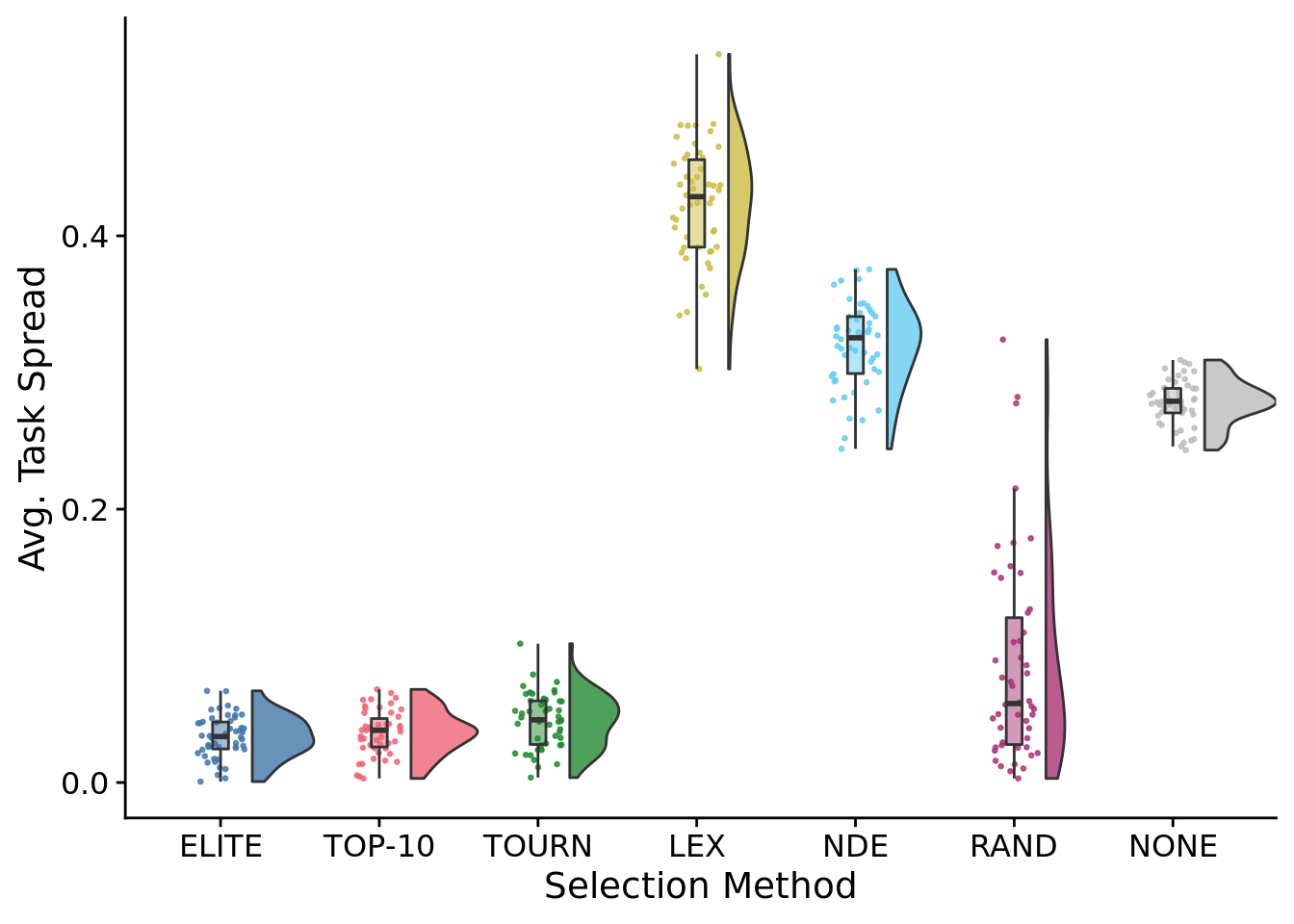
ggsave(
plot=task_profile_spread_fig,
paste0(plot_directory, "2021-11-30-task-profile-spread.pdf")
)## Saving 7 x 5 in imageStatistical results:
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: avg_cosine_dist_from_centroid by SELECTION_METHOD
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 281.91, df = 6, p-value < 2.2e-16# Kruskal-wallis is significant, so we do a post-hoc wilcoxon rank-sum.
pairwise.wilcox.test(
x=exp_summary_data$avg_cosine_dist_from_centroid,
g=exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
p.adjust.method="bonferroni",
)##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: exp_summary_data$avg_cosine_dist_from_centroid and exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD
##
## elite elite-10 tourn lex nde random
## elite-10 1.0000 - - - - -
## tourn 0.0644 0.6009 - - - -
## lex < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 - - -
## nde < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 7.5e-15 - -
## random 0.0015 0.0121 0.4682 < 2e-16 1.3e-15 -
## none < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 3.7e-09 5.4e-14
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni8.6.3 Task profile entropy
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=SELECTION_METHOD,
y=pop_trait_profile_entropy,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(height=0, width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Shannon entropy of task profiles"
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_fill_fun(
) +
scale_color_fun(
) +
theme(
legend.position="none"
)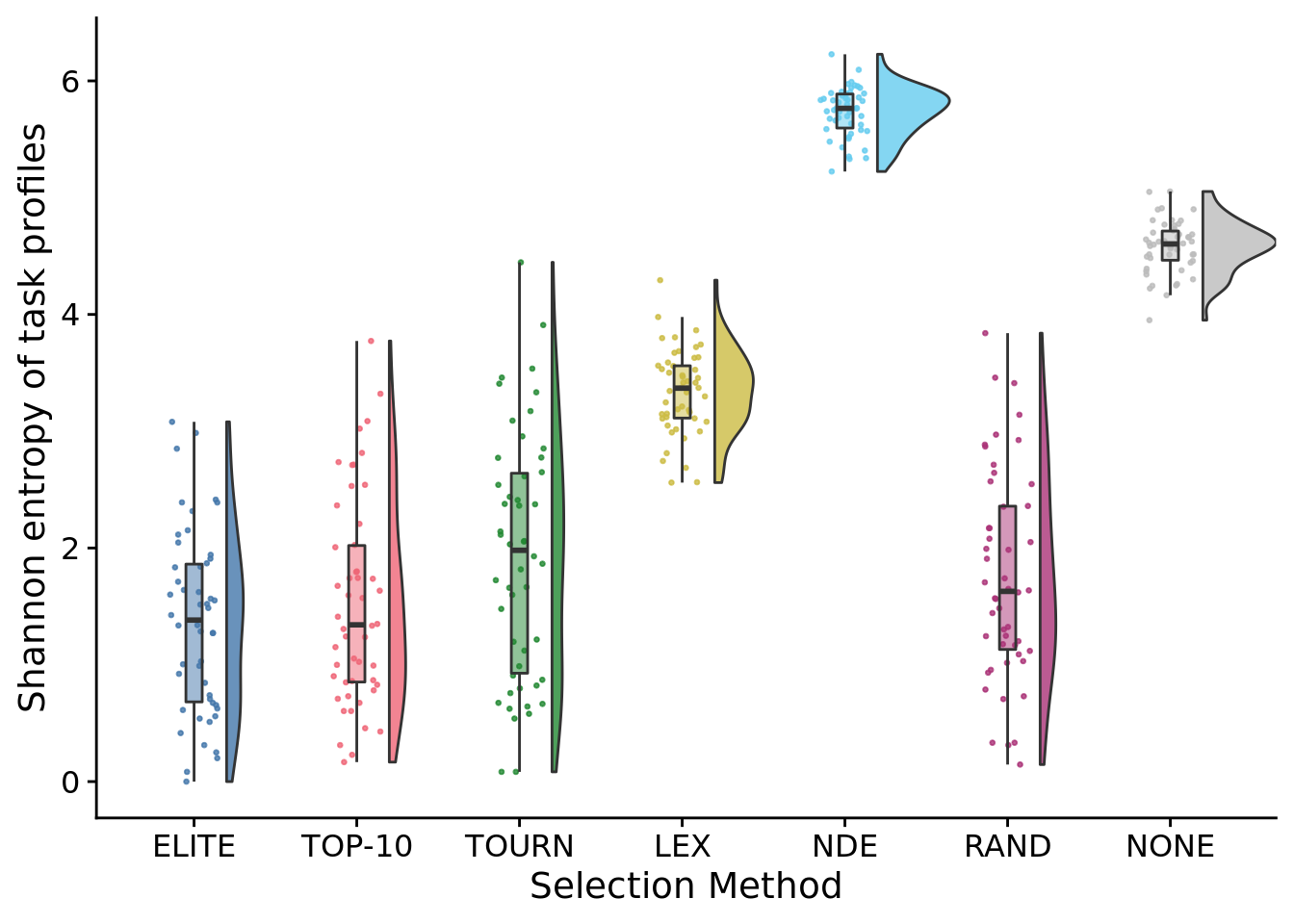
## Saving 7 x 5 in imageStatistical results:
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: pop_trait_profile_entropy by SELECTION_METHOD
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 271.97, df = 6, p-value < 2.2e-16pairwise.wilcox.test(
x=exp_summary_data$pop_trait_profile_entropy,
g=exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
p.adjust.method="bonferroni",
)##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: exp_summary_data$pop_trait_profile_entropy and exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD
##
## elite elite-10 tourn lex nde random
## elite-10 1.00 - - - - -
## tourn 0.12 1.00 - - - -
## lex 5.2e-16 5.1e-14 2.4e-10 - - -
## nde < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 - -
## random 0.77 1.00 1.00 6.2e-13 < 2e-16 -
## none < 2e-16 < 2e-16 3.0e-16 2.3e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni8.7 Task coverage per N populations
We analyzed the (maximum) number of tasks added to metapopulation task coverage for a given number (N) of member populations considered. That is, for each N, we solved the maximum set coverage problem for task coverage: what is the maximum number of tasks that can be covered given N populations from this metapopulation?
ggplot(
task_coverage_per_pop_data,
aes(
x=n_pops,
y=max_tasks_covered,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD,
color=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
stat_summary(geom="line", fun=mean) +
stat_summary(
geom="ribbon",
fun.data="mean_cl_boot",
fun.args=list(conf.int=0.95),
alpha=0.2,
linetype=0
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Maximum task coverage"
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Number of populations",
limits=c(0, 15)
) +
scale_fill_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_color_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
theme(
legend.position="bottom"
)## Warning: Removed 28350 rows containing non-finite values (stat_summary).
## Removed 28350 rows containing non-finite values (stat_summary).## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`: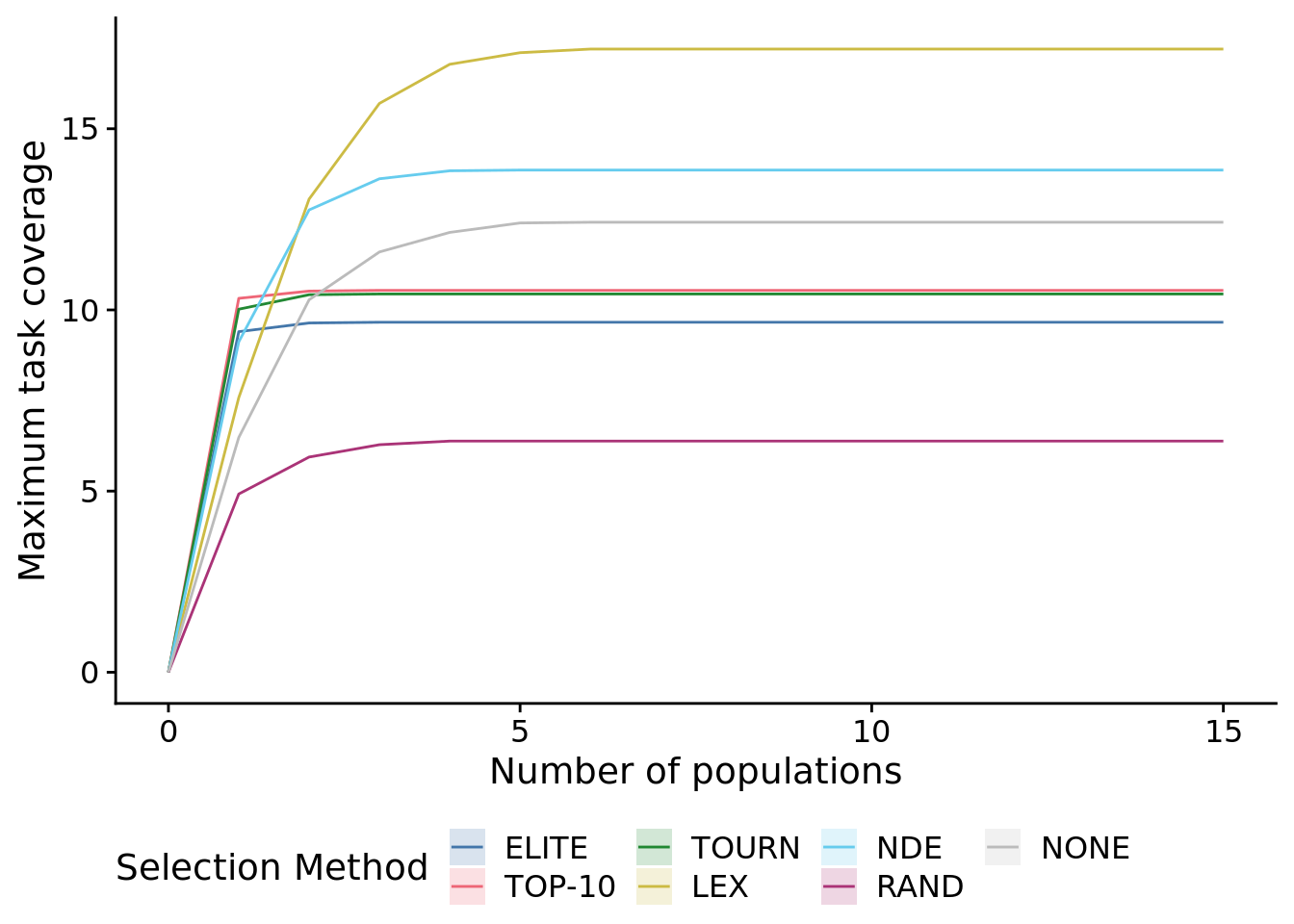
## Warning: Removed 28350 rows containing non-finite values (stat_summary).## Warning: Removed 28350 rows containing non-finite values (stat_summary).## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`:8.8 Average number of different populations selected per generation
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=SELECTION_METHOD,
y=avg_unique_selected,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(height=0, width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Avg. number selected"
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_fill_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_color_fun(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
theme(
legend.position="none"
)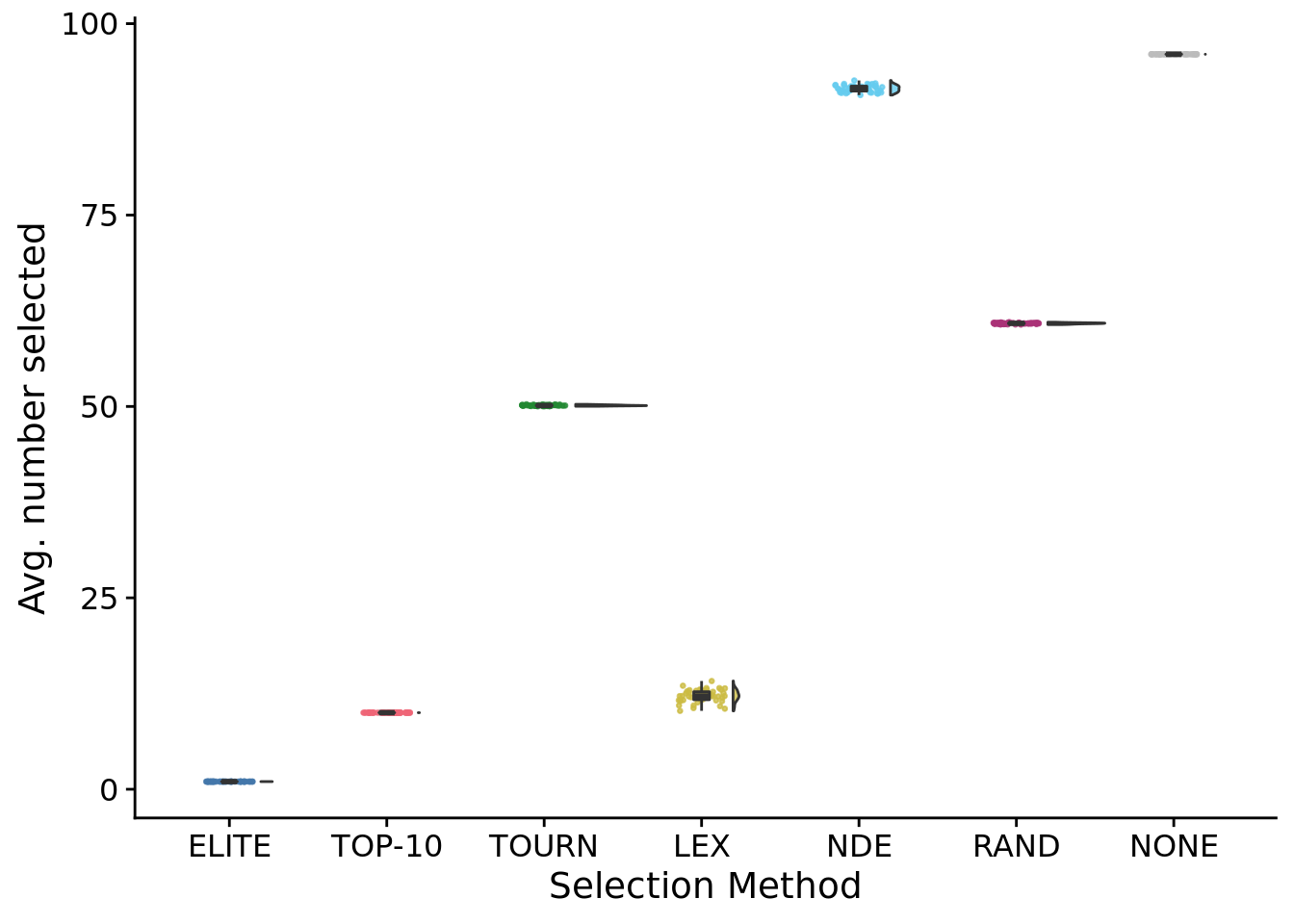
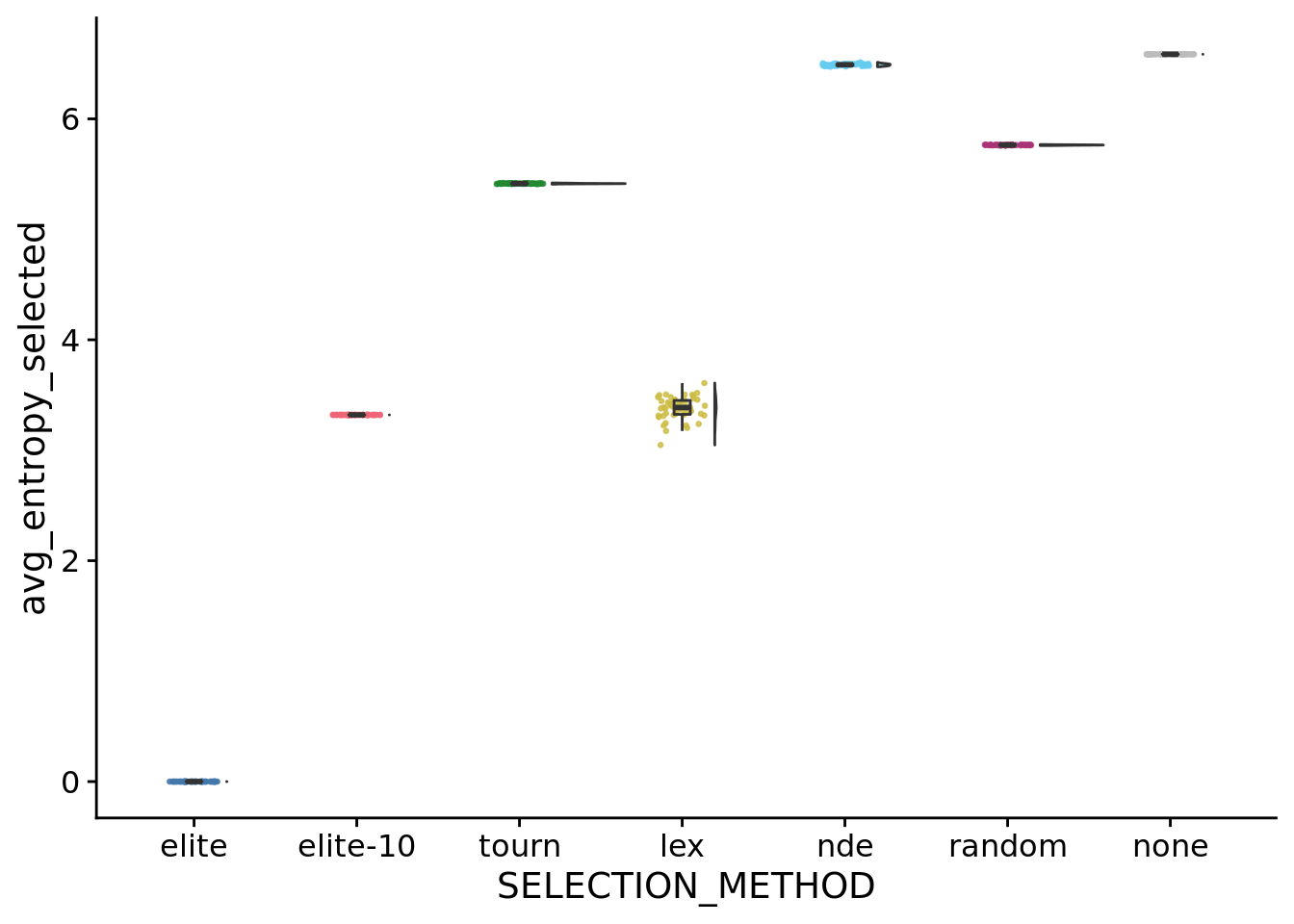
## Saving 7 x 5 in image## [1] 1## [1] 10## [1] 50.1328## [1] 91.50978## [1] 12.18061## [1] 60.847748.8.1 Entropy of selected population IDs
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=SELECTION_METHOD,
y=avg_entropy_selected,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(height=0, width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_fill_fun(
) +
scale_color_fun(
) +
theme(
legend.position="none"
)
8.9 Average number of organisms in populations at end of maturation period
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=SELECTION_METHOD,
y=avg_num_orgs,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Average number of organisms",
limits=c(950, 1000)
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_fill_fun(
) +
scale_color_fun(
) +
theme(
legend.position="none"
)## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing non-finite values (stat_ydensity).## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing non-finite values (stat_boxplot).## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_point).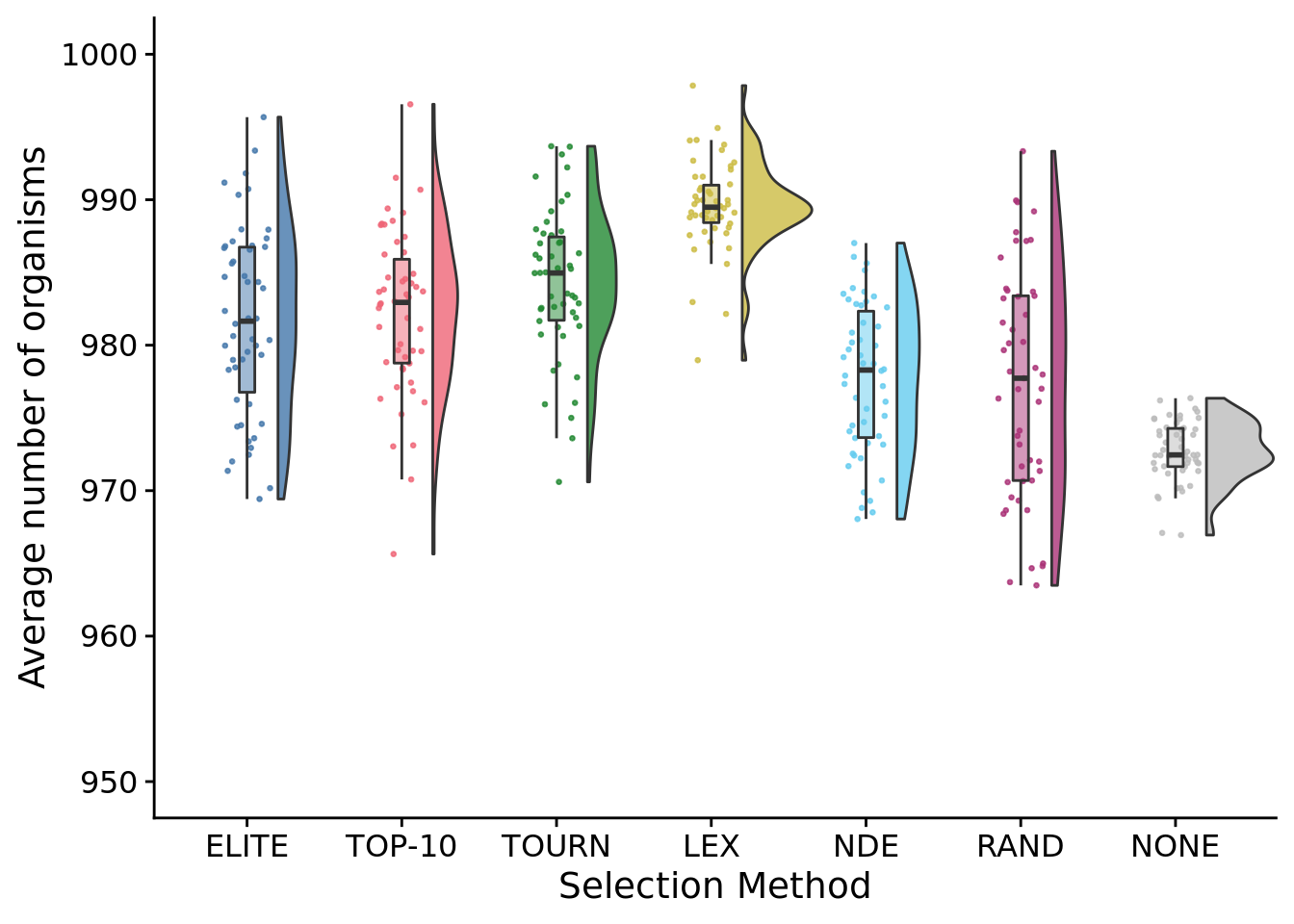
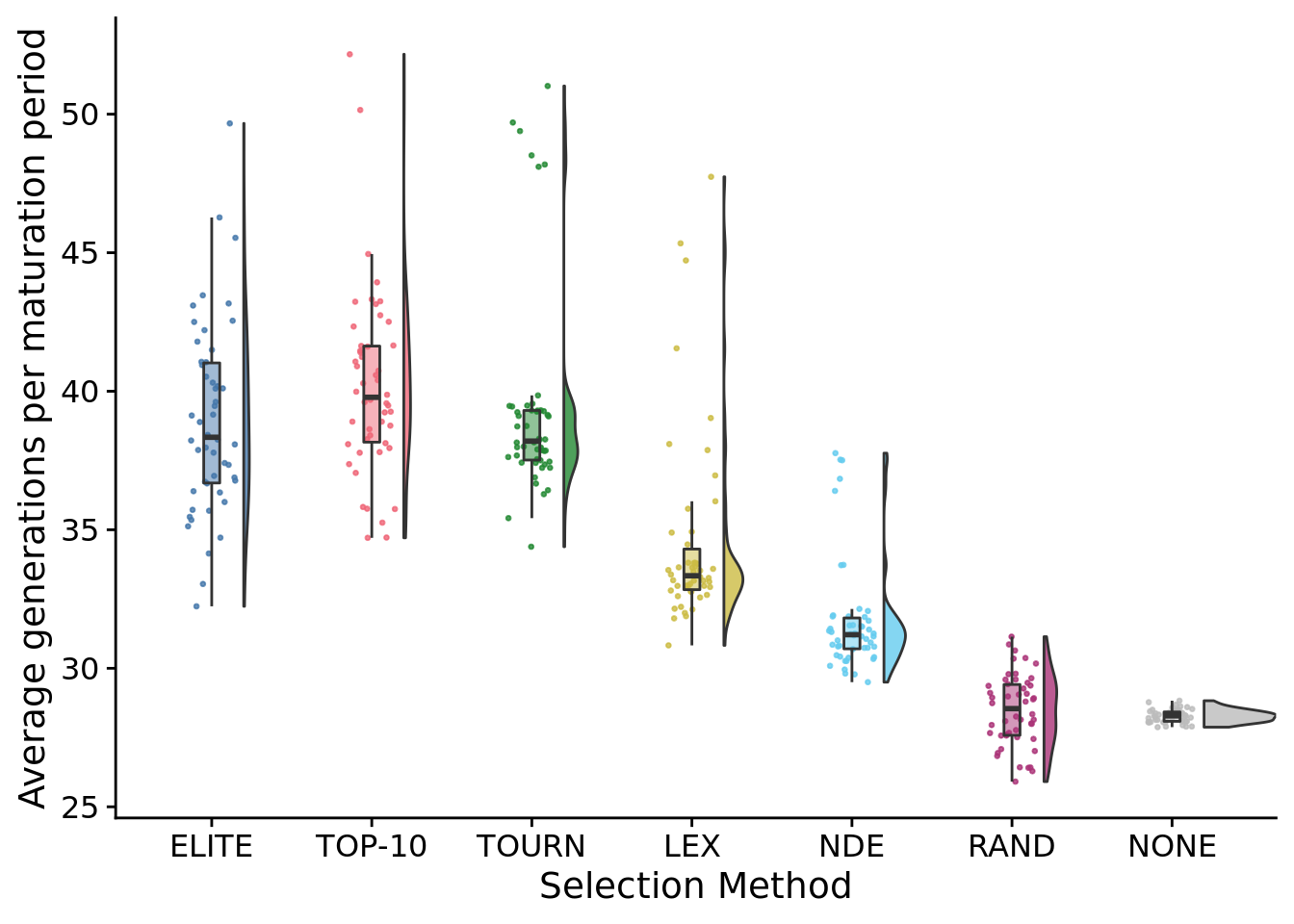
## Saving 7 x 5 in image## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing non-finite values (stat_ydensity).## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing non-finite values (stat_boxplot).## Warning: Removed 1 rows containing missing values (geom_point).8.10 Average generations per maturation period
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=SELECTION_METHOD,
y=avg_gens,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Average generations per maturation period"
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Selection Method",
breaks=selection_method_breaks,
labels=selection_method_labels
) +
scale_fill_fun(
) +
scale_color_fun(
) +
theme(
legend.position="none"
)
## Saving 7 x 5 in imagemedian(exp_summary_data$total_gens_approx) # Used for determining how many generations to run EC for## [1] 65922.48.11 Manuscript figures
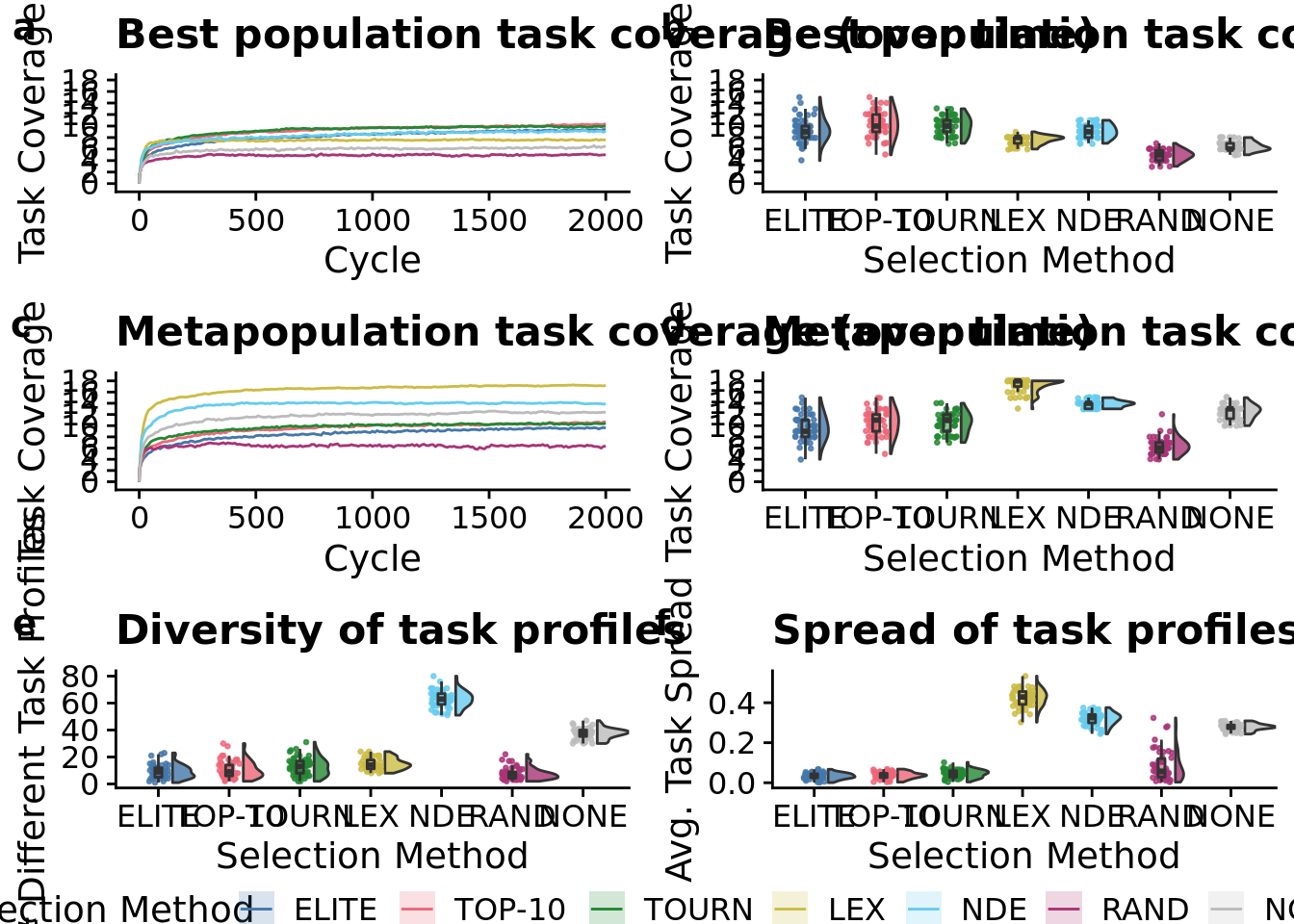
Without time series:
# NOTE - This is just a rough draft!
grid <- plot_grid(
max_trait_cov_fig +
theme(
axis.title.x=element_blank(),
axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9)
) +
ggtitle("Best population task coverage"),
total_trait_cov_fig +
theme(
axis.title.x=element_blank(),
axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9)
) +
ggtitle("Metapopulation task coverage"),
num_pop_task_profiles_fig +
theme(
axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9)
) +
ggtitle("Diversity of task profiles"),
task_profile_spread_fig +
theme(
axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9)
) +
ggtitle("Spread of task profiles"),
nrow=2,
ncol=2,
labels="auto"
)
grid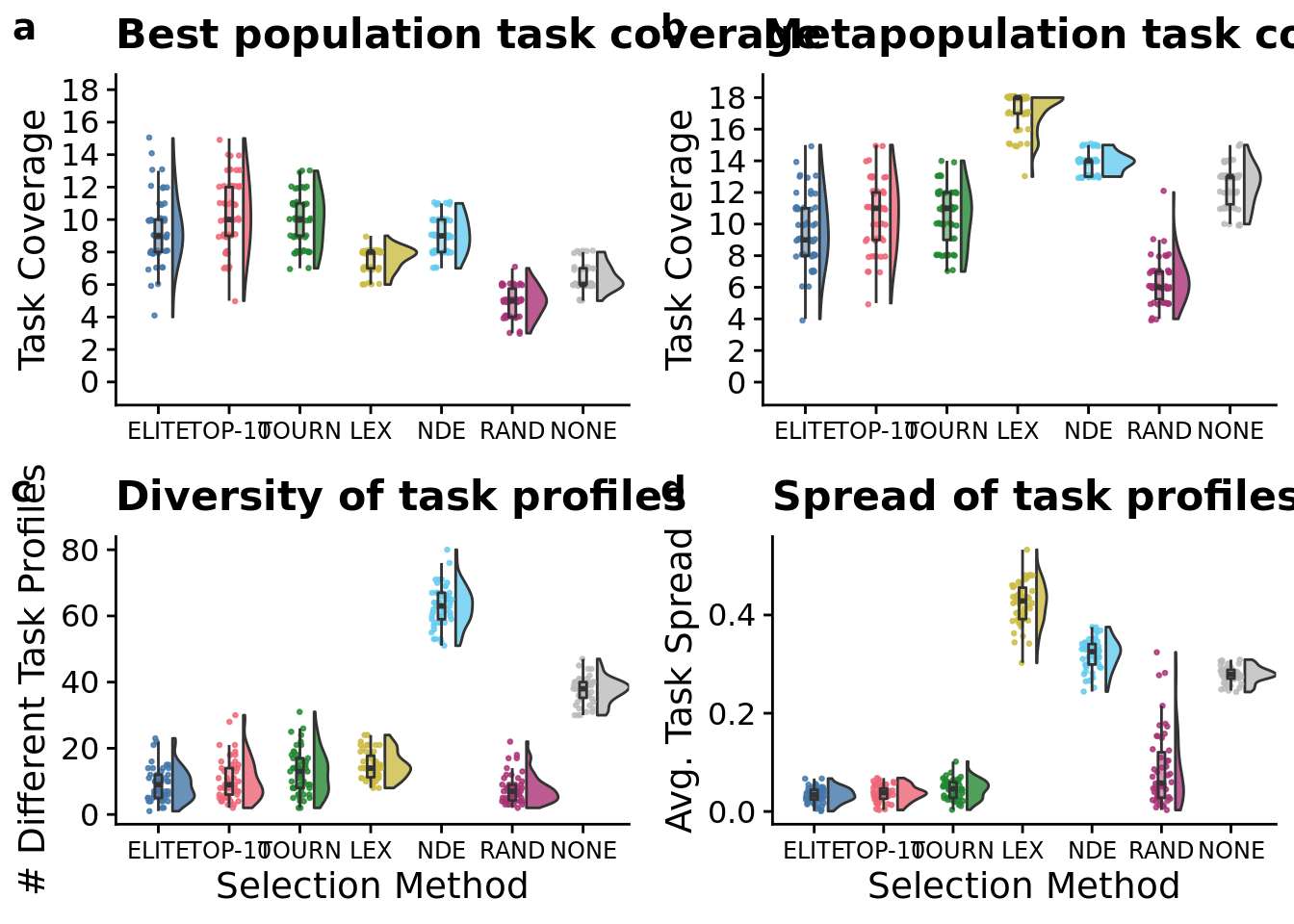
save_plot(
filename=paste0(plot_directory, "2021-11-30-selection-figure.pdf"),
plot=grid,
base_height=6
)With time series:
legend <- cowplot::get_legend(
max_trait_cov_ot_fig +
guides(
color=guide_legend(nrow=1),
fill=guide_legend(nrow=1)
) +
theme(
legend.position = "bottom",
legend.box="horizontal",
legend.justification="center"
)
)## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`:max_trait_cov_row <- plot_grid(
max_trait_cov_ot_fig +
ggtitle("Best population task coverage (over time)") +
theme(
legend.position="none"
# plot.title=element_text(size=12),
# axis.text=element_text(size=10),
# axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9),
# axis.title.y = element_text(size = 10)
),
max_trait_cov_fig +
ggtitle("Best population task coverage (final)"),
theme(
legend.position="none"
# plot.title=element_text(size=12),
# axis.text=element_text(size=10),
# axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9),
# axis.title.y = element_text(size = 10)
),
nrow=1,
ncol=2,
align="h",
labels=c("a", "b")
# rel_widths=c(3,2),
)## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`:## Warning in as_grob.default(plot): Cannot convert object of class themegg into a
## grob.## Warning: Graphs cannot be horizontally aligned unless the axis parameter is set.
## Placing graphs unaligned.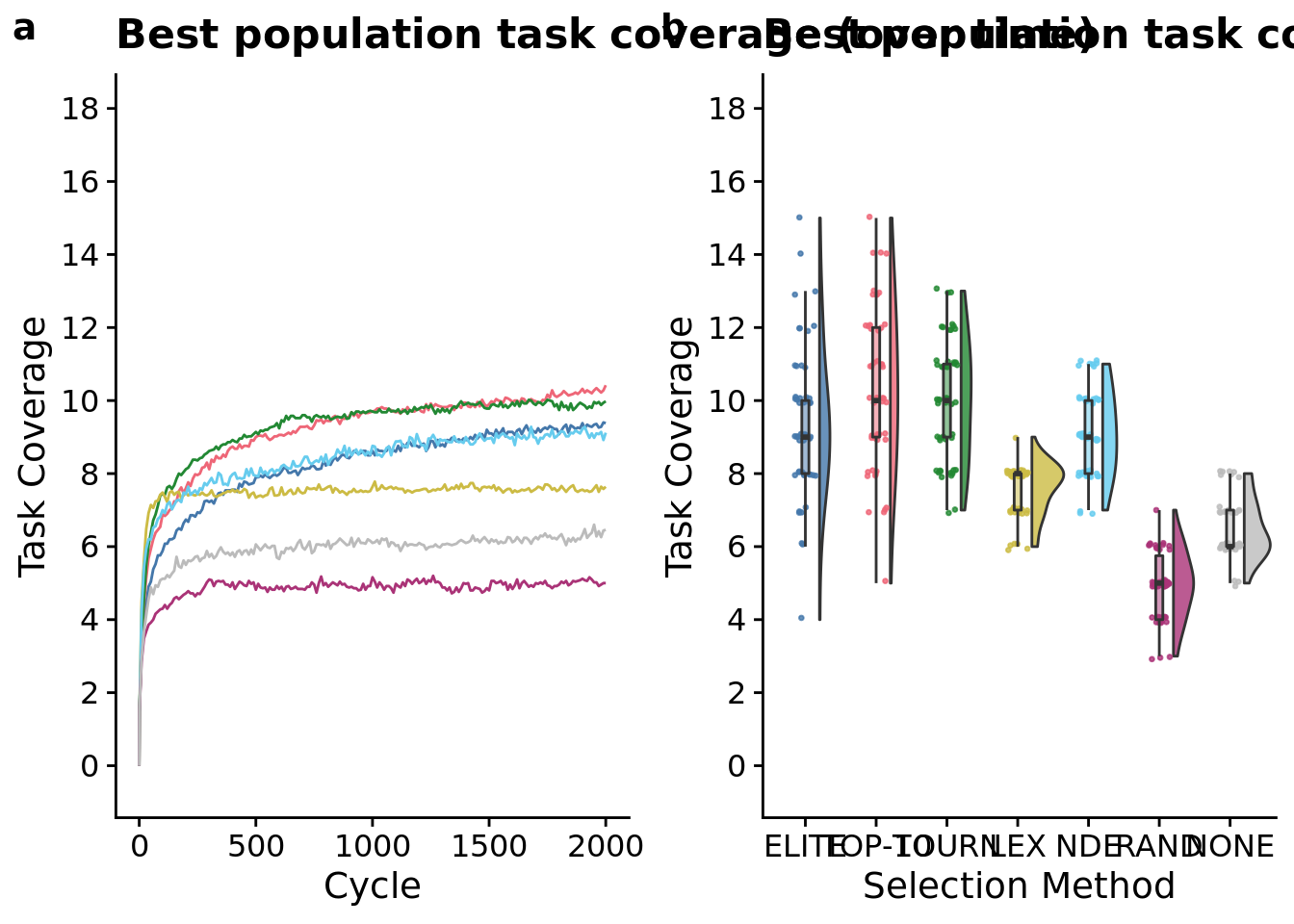
total_trait_cov_row <- plot_grid(
metapop_task_cov_ot_fig +
ggtitle("Metapopulation task coverage (over time)") +
theme(
legend.position="none"
# plot.title=element_text(size=12),
# axis.text=element_text(size=10),
# axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9),
# axis.title.y = element_text(size = 10)
),
total_trait_cov_fig +
ggtitle("Metapopulation task coverage (final)"),
theme(
legend.position="none"
# plot.title=element_text(size=12),
# axis.text=element_text(size=10),
# axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9),
# axis.title.y = element_text(size = 10)
),
nrow=1,
ncol=2,
align="h",
labels=c("c", "d")
# rel_widths=c(3,2),
)## Warning: Computation failed in `stat_summary()`:## Warning in as_grob.default(plot): Cannot convert object of class themegg into a
## grob.## Warning: Graphs cannot be horizontally aligned unless the axis parameter is set.
## Placing graphs unaligned.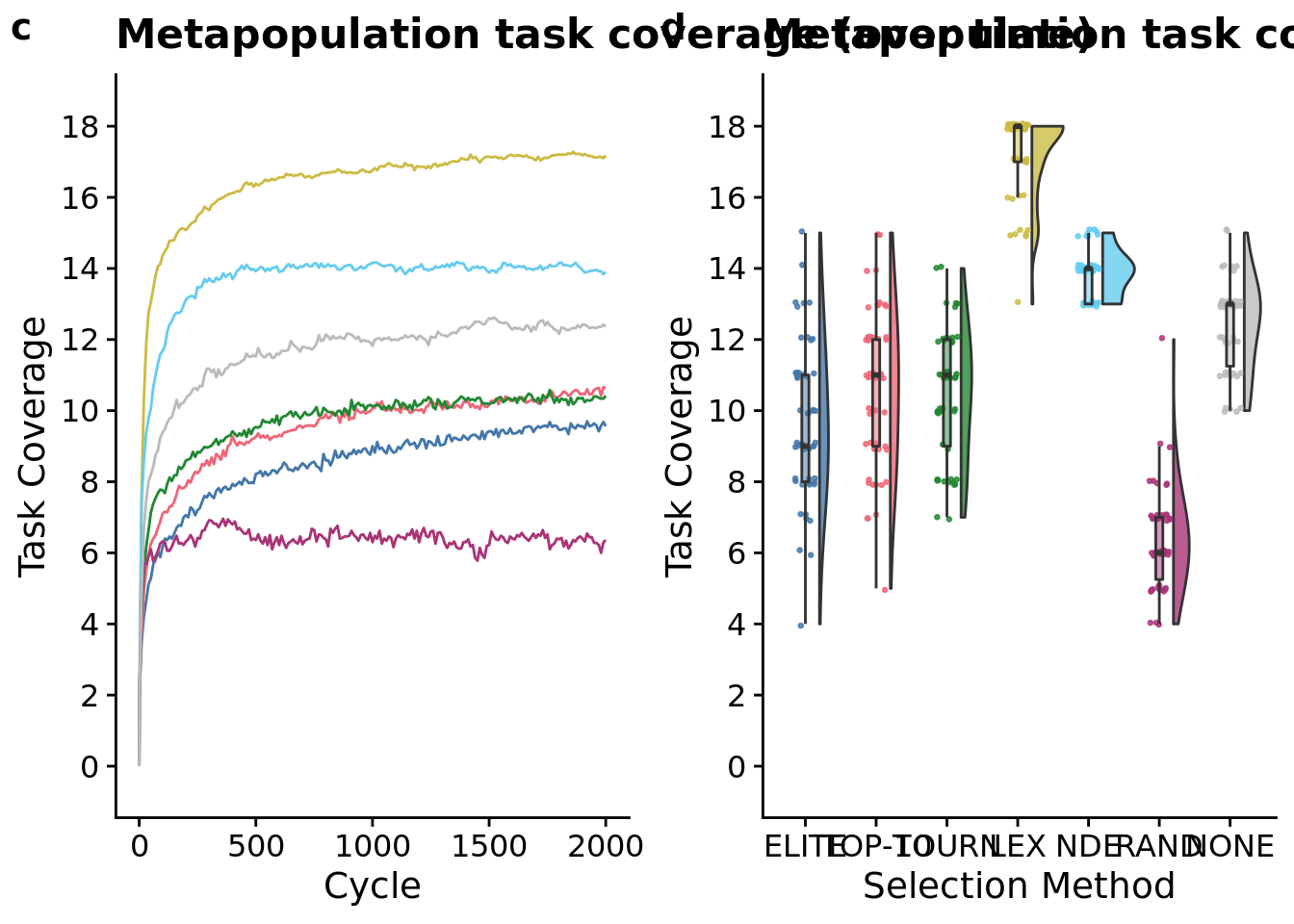
diversity_row <- plot_grid(
num_pop_task_profiles_fig +
ggtitle("Diversity of task profiles") +
theme(
legend.position="none"
# plot.title=element_text(size=12),
# axis.text=element_text(size=10),
# axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9),
# axis.title.y = element_text(size = 10)
),
task_profile_spread_fig +
ggtitle("Spread of task profiles"),
theme(
legend.position="none"
# plot.title=element_text(size=12),
# axis.text=element_text(size=10),
# axis.text.x = element_text(size = 9),
# axis.title.y = element_text(size = 10)
),
nrow=1,
ncol=2,
align="h",
labels=c("e", "f")
# rel_widths=c(3,2),
)## Warning in as_grob.default(plot): Cannot convert object of class themegg into a
## grob.
## Warning in as_grob.default(plot): Graphs cannot be horizontally aligned unless
## the axis parameter is set. Placing graphs unaligned.# diversity_row
grid <- plot_grid(
max_trait_cov_row,
total_trait_cov_row,
diversity_row,
legend,
nrow=4,
ncol=1,
rel_heights=c(1, 1, 1, 0.1)
)
grid