Chapter 11 Population propagule sample size
In this preliminary experiment, we looked at the effect of varying the size of propagules used when creating “offspring” populations from “parent” populations.
We conducted these exploratory experiments well before the final set of experiments presented in our manuscript, so their setups are not the same:
- We only compared elite, lexicase, non-dominated elite, and a no selection control.
- The environment is simpler with 8 population-level functions instead of 18.
- The maximum population size is 900 instead of 1,000.
- The maturation period is longer (300 updates versus 200)
- We ran the experiment for fewer cycles (500 instead of 2,000).
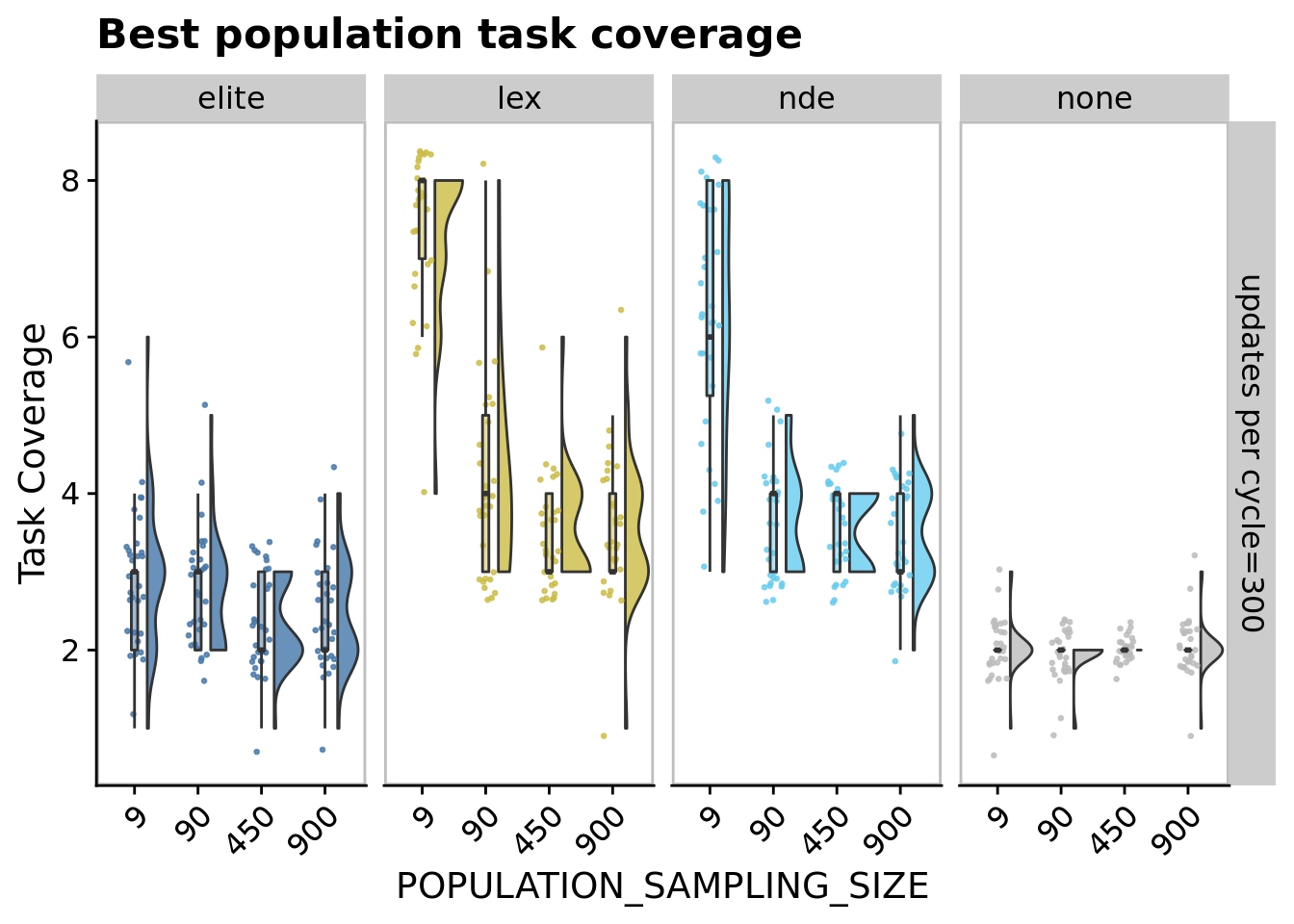
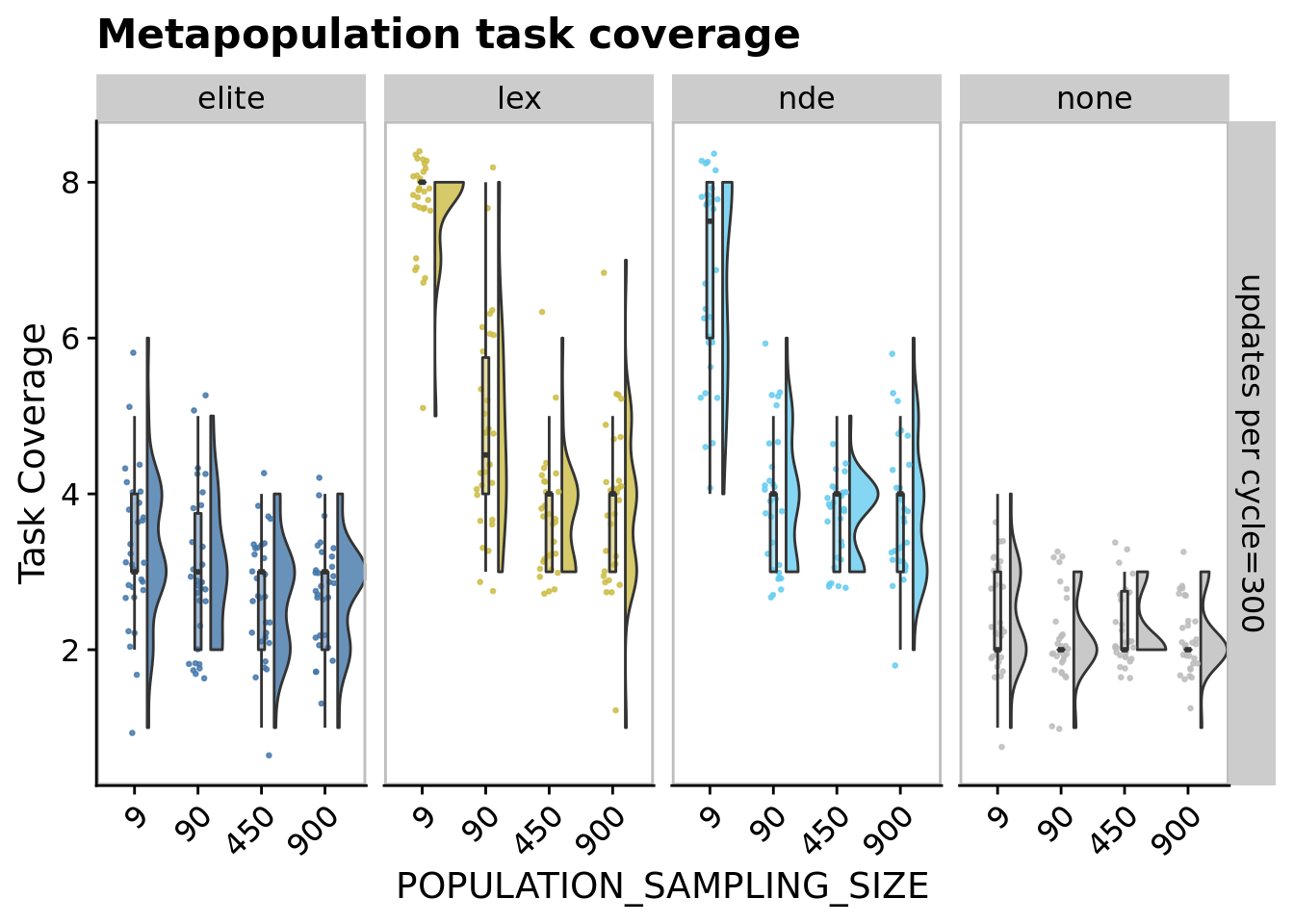
Overall, we found that the effect of propagule size varied by selection scheme. For elite selection and the no-selection control, sample size had little effect. For lexicase and non-dominated elite selection, the smallest propagule size (1% of the maximum population size) resulted in significantly better outcomes than using larger propagule sizes (e.g., 100% of the maximum population size).
Because these data were collected during early experiments, we tracked fewer population/metapopulation statistics. Future work should further investigate the effects of propagule size, especially in the context of more complex environments that support more complex organism-organism interaction.
11.2 Analysis dependencies
Load all required R libraries
library(tidyverse)
library(ggplot2)
library(cowplot)
library(RColorBrewer)
library(scales)
library(khroma)
source("https://gist.githubusercontent.com/benmarwick/2a1bb0133ff568cbe28d/raw/fb53bd97121f7f9ce947837ef1a4c65a73bffb3f/geom_flat_violin.R")These analyses were knit with the following environment:
## _
## platform x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
## arch x86_64
## os linux-gnu
## system x86_64, linux-gnu
## status
## major 4
## minor 2.1
## year 2022
## month 06
## day 23
## svn rev 82513
## language R
## version.string R version 4.2.1 (2022-06-23)
## nickname Funny-Looking Kid11.3 Setup
Experiment summary data
exp_summary_data_loc <- paste0(working_directory,"data/experiment_summary.csv")
exp_summary_data <- read.csv(exp_summary_data_loc, na.strings="NONE")
# Mark factors
exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD <- factor(
exp_summary_data$SELECTION_METHOD,
levels=c(
"elite",
"tournament",
"lexicase",
"non-dominated-elite",
"non-dominated-tournament",
"random",
"none"
),
labels=c(
"elite",
"tournament",
"lex",
"nde",
"ndt",
"random",
"none"
)
)
exp_summary_data$NUM_POPS <- factor(
exp_summary_data$NUM_POPS,
levels=c(
"24",
"48",
"96"
)
)
exp_summary_data$UPDATES_PER_EPOCH <- as.factor(
exp_summary_data$UPDATES_PER_EPOCH
)
exp_summary_data$POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE <- as.factor(
exp_summary_data$POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE
)
exp_summary_data$SAMPLE_SIZE <- exp_summary_data$POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE
exp_summary_data <- filter(exp_summary_data, UPDATES_PER_EPOCH=="300")Miscellaneous setup
# Configure our default graphing theme
theme_set(theme_cowplot())
# Create a directory to store plots
plot_directory <- paste0(working_directory, "plots/")
dir.create(plot_directory, showWarnings=FALSE)
selection_methods_smaller_set_colors <- c("#4477AA", "#CCBB44", "#66CCEE", "#BBBBBB")
sel.labs <- c(
"elite",
"tournament",
"lex",
"nde",
"ndt",
"random",
"none"
)
names(sel.labs) <- c(
"elite",
"tournament",
"lex",
"nde",
"ndt",
"random",
"none"
)
upe.labs <- c(
"updates per cycle=100",
"updates per cycle=300"
)
names(upe.labs) <- c(
"100",
"300"
)11.4 Average number of organisms
Average number of organisms per world at the end of a run.
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE,
y=avg_num_orgs,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_fill_manual(
values=selection_methods_smaller_set_colors
) +
scale_color_manual(
values=selection_methods_smaller_set_colors
) +
facet_grid(
UPDATES_PER_EPOCH~SELECTION_METHOD,
labeller = labeller(UPDATES_PER_EPOCH=upe.labs, SELECTION_METHOD=sel.labs)
) +
theme(
legend.position="none",
axis.text.x=element_text(angle=45,hjust=1)
)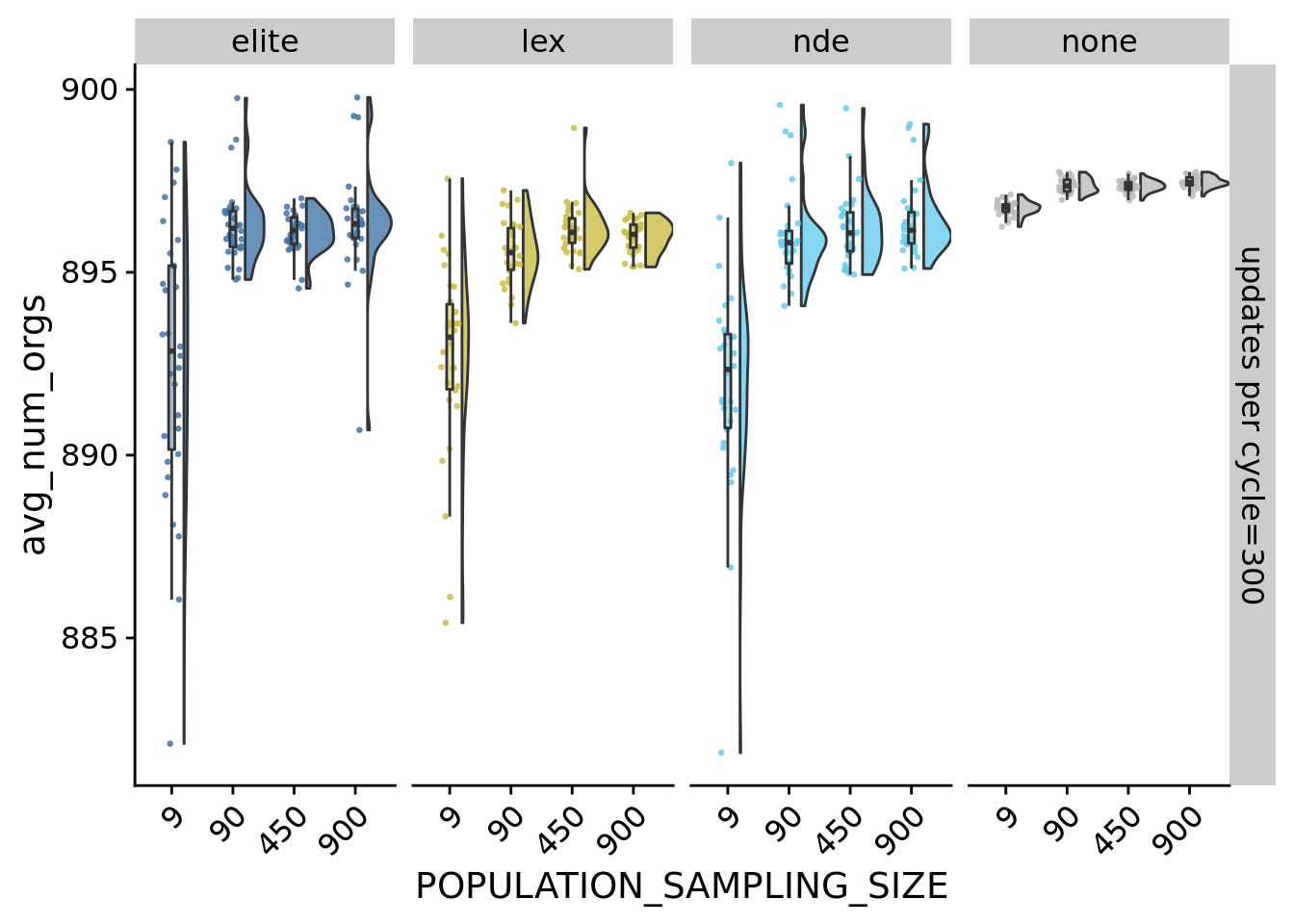
## Saving 7 x 5 in imageIn general, the smaller propagule sizes are less likely to reach 900 organisms during the maturation period. However, all final population sizes are within 25 organisms of each, so no substantial differences here.
11.5 Average generations per maturation period
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE,
y=avg_gens,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_fill_manual(
values=selection_methods_smaller_set_colors
) +
scale_color_manual(
values=selection_methods_smaller_set_colors
) +
facet_grid(
UPDATES_PER_EPOCH~SELECTION_METHOD,
labeller = labeller(UPDATES_PER_EPOCH=upe.labs, SELECTION_METHOD=sel.labs)
) +
theme(
legend.position="none",
axis.text.x=element_text(angle=45,hjust=1)
)
11.6 Performance
11.6.1 Best population task coverage
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE,
y=max_trait_coverage,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Task Coverage"
) +
scale_fill_manual(
values=selection_methods_smaller_set_colors
) +
scale_color_manual(
values=selection_methods_smaller_set_colors
) +
facet_grid(
UPDATES_PER_EPOCH~SELECTION_METHOD,
labeller = labeller(UPDATES_PER_EPOCH=upe.labs, SELECTION_METHOD=sel.labs)
) +
ggtitle("Best population task coverage") +
theme(
legend.position="none",
axis.text.x=element_text(angle=45,hjust=1),
panel.border=element_rect(colour="grey",size=1)
)
comp_data <- filter(
exp_summary_data,
SELECTION_METHOD=="lex"
)
kruskal.test(
formula=max_trait_coverage~POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE,
data=comp_data
)##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: max_trait_coverage by POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 69.574, df = 3, p-value = 5.266e-15pairwise.wilcox.test(
x=comp_data$max_trait_coverage,
g=comp_data$POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE,
p.adjust.method="bonferroni",
exact=FALSE
)##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: comp_data$max_trait_coverage and comp_data$POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE
##
## 9 90 450
## 90 5.8e-09 - -
## 450 1.1e-10 0.091 -
## 900 1.6e-10 0.241 1.000
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni11.6.2 Metapopulation task coverage
ggplot(
exp_summary_data,
aes(
x=POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE,
y=total_trait_coverage,
fill=SELECTION_METHOD
)
) +
geom_flat_violin(
position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0),
alpha = .8
) +
geom_point(
mapping=aes(color=SELECTION_METHOD),
position = position_jitter(width = .15),
size = .5,
alpha = 0.8
) +
geom_boxplot(
width = .1,
outlier.shape = NA,
alpha = 0.5
) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Task Coverage"
) +
scale_fill_manual(
values=selection_methods_smaller_set_colors
) +
scale_color_manual(
values=selection_methods_smaller_set_colors
) +
facet_grid(
UPDATES_PER_EPOCH~SELECTION_METHOD,
labeller = labeller(UPDATES_PER_EPOCH=upe.labs, SELECTION_METHOD=sel.labs)
) +
ggtitle("Metapopulation task coverage") +
theme(
legend.position="none",
axis.text.x=element_text(angle=45,hjust=1),
panel.border=element_rect(colour="grey",size=1)
)
comp_data <- filter(
exp_summary_data,
SELECTION_METHOD=="lex"
)
kruskal.test(
formula=total_trait_coverage~POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE,
data=comp_data
)##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: total_trait_coverage by POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 74.497, df = 3, p-value = 4.644e-16pairwise.wilcox.test(
x=comp_data$total_trait_coverage,
g=comp_data$POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE,
p.adjust.method="bonferroni",
exact=FALSE
)##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: comp_data$total_trait_coverage and comp_data$POPULATION_SAMPLING_SIZE
##
## 9 90 450
## 90 2.2e-09 - -
## 450 2.3e-11 0.0012 -
## 900 5.3e-11 0.0279 1.0000
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni